The translation of this document is outdated.
Translation validity: 24.02.2021.–04.04.2024.
Amendments not included:
26.03.2024.
Text consolidated by Valsts valodas centrs (State
Language Centre) with amending regulations of:
1 February 2011 [shall come
into force from 4 February 2011];
7 April 2015 [shall come into force from 1 June
2015];
10 July 2018 [shall come into force from 13 July
2018];
7 January 2020 [shall come into force from 17 January
2020];
18 February 2021 [shall come into force from 24 February
2021].
If a whole or part of a paragraph has been amended,
the date of the amending regulation appears in square
brackets at the end of the paragraph. If a whole
paragraph or sub-paragraph has been deleted, the date of
the deletion appears in square brackets beside the
deleted paragraph or sub-paragraph.
|
|
Republic of Latvia
Cabinet
Regulation No. 325
Adopted 15 May 2007
|
Labour Protection Requirements
when Coming in Contact with Chemical Substances at
Workplaces
Issued pursuant to
Section 25, Clause 11 of the Labour Protection Law and
Section 16 of the Chemical Substances Law
[1 February 2011]
I. General Provisions
1. This Regulation prescribes labour protection requirements
for employees when coming in contact with chemical substances
(including mixtures) at workplaces if a risk is caused or may be
caused from the effect of chemical substances present in the work
environment or related to the working process, as well as special
restrictions and prohibitions in relation to individual dangerous
chemical substances or mixtures.
[1 February 2011]
2. This Regulation applies to workplaces where an employee is
or may be exposed to the effect of such chemical substances and
mixtures:
2.1. which conforms to the criteria laid down in Annex 1 to
Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of
the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and
packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing
Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation
(EC) No 1907/2006 (hereinafter - Regulation No 1272/2008) for
classification of substances in any of physical or health hazard
classes irrespective of whether this chemical substance is
classified in accordance with Regulation No 1272/2008;
2.2. which are present in the working environment or utilised
at work and due to the physical, chemical and toxic properties
thereof endanger the safety and health of an employee;
2.3. to which an occupational exposure limit value (OEV) has
been determined - such concentration of chemical substances or
mixtures in the air of the work environment which for the whole
duration of the life of an employee does not cause the
contraction of a disease or deterioration of health which can be
determined by modern investigative methods if the relevant
chemical substances and mixtures affect an employee not longer
than 8 hours during a working day or not longer than 40 hours a
week (Annex 1, 2); and
2.4. to which a biological limit value (BLV) has been
determined - indicators of concentration of chemical substances
and metabolites thereof received by the organism of the employee
and the biological effects caused by chemical substances in the
biological environment of the employee, which values shall be
determined for healthy employees who are exposed to chemical
substances and mixtures on the level of the occupational exposure
limit value (OEV) (Annex 3).
[1 February 2011; 7 April 2015]
3. The occupational exposure limit value (OEV) for a chemical
substance shall be determined taking into account
physico-chemical properties, toxicity, epidemiological researches
in the field of non-infectious diseases and conditions for
technological process, as well as evaluating the data regarding
chemical substances with a similar structure. The occupational
exposure limit value (OEV) of a chemical substance shall be used
for evaluation of chemical risk on the working environment
(concentration of the chemical substance in the air of the
working environment shall be compared with the occupational
exposure limit value (OEV)).
4. The occupational exposure limit value (OEV) shall be
defined as an average arithmetical value for a working day of 8
hours (average shift concentration) or as a value for a short
period of time (up to 15 min., for fibrogenic substances - up to
30 min.). The occupational exposure limit value (OEV) shall be
measured at a temperature of 20 oC at a pressure of
101.3 kPa and expressed in milligrams per cubic meter
(mg/m3), but the concentration of gases and vapour may
be expressed also in measurement units not dependent on the
temperature and pressure - ppm (ml/m3), which is a
millionth of the capacity.
5. The Ministry of Welfare shall, in co-operation with the
relevant standards technical committee, recommend to the State
limited liability company "Standardisation, Accreditation and
Metrology Centre" a list of standards to be drawn up, adapted and
applied in relation to this Regulation.
[17 April 2015]
6. The State limited liability company "Standardisation,
Accreditation and Metrology Centre" shall publish on its official
web page a list of those Latvian national standards applied to
ensure the conformity with the requirements laid down in this
Regulation (hereinafter - the applicable standards).
[7 April 2015]
7. The employer shall be liable for compliance with this
Regulation.
8. Compliance with this Regulation shall be controlled by the
State Labour Inspectorate and other authorities in accordance
with the competence specified thereto by the Chemical Substances
Law.
[1 February 2011]
II. Determination and Assessment
of Risk
9. The employer shall ensure the assessment of the risk caused
by chemical substances and mixtures in conformity with the
procedures for the internal supervision of the work environment
and the procedures for the risk assessment in the work
environment of an undertaking involving trusted representatives
and employees.
[1 February 2011]
10. To determine the concentration of chemical substances in
the air of the work environment, the employer shall, upon request
of the control authorities referred to in Paragraph 8 of this
Regulation, involve the laboratory accredited in the national
accreditation body in accordance with the laws and regulations
regarding the assessment, accreditation, and surveillance of
conformity assessment bodies, or in an accreditation body of
another European Union Member State or European Economic Area
State which performs the conformity assessment of laboratories in
specification of the concentration of chemical substances in the
air of the work environment.
[7 April 2015]
11. The employer shall determine workplaces and work processes
where chemical substances and mixtures cause or may cause a risk
to the safety and health of employees, and assess the risk
thereof, taking into account:
11.1. information in the safety data sheets of the chemical
substances and mixtures received from a supplier or importer;
11.2. results of the health examination of employees;
11.3. results and prognoses of preventative measures taken or
to be taken;
11.4. other information regarding the dangerousness of the
chemical substances and mixtures;
11.5. the occupational exposure limit value (OEV) of chemical
substances in the air of the work environment;
11.6. the biological limit values (BLV) of chemical substances
and mixtures;
11.7. particular work conditions and processes at a workplace
and in a room (including at adjacent workplaces), as well as
dangerous properties of chemical substances and mixtures present
in the work environment due to which the risk is caused or
increased to the health and safety of employees in the relevant
work conditions and in emergency situations;
11.8. the occupational exposure concentration of chemical
substances in the air of the work environment, which is specified
as 8 hours or temporary occupational exposure concentration (one
or both of these values), as well as the type and duration of the
effect of substances;
11.9. the amount of chemical substances and mixtures at the
workplace;
11.10. risk of potential accidents which is related to the use
of chemical substances and mixtures at work and the
physico-chemical properties thereof:
11.10.1. if there are binding regulatory enactments regarding
the procedures for the industrial accident risk assessment and
risk reduction measures for the undertaking, then, in carrying
out the procedures specified therein, also the requirements
specified in this Regulation shall be taken into account; or
11.10.2. if there are no binding regulatory enactments
regarding the procedures for the industrial accident risk
assessment and risk reduction measures for the undertaking, the
accident risk reduction measures shall be determined by this
Regulation; and
11.11. the results of other risk assessments (for example, the
risk assessment of a new chemical substance or risk assessment of
an accident).
[1 February 2011]
12. Risk shall be assessed regularly once a year, as well as
in cases when:
12.1. significant changes have occurred in the work
environment (for example, changes in the composition, physical
state or raw materials of a preparation);
12.2. new activities have been introduced or the production
process has been modified (for example, work equipment,
technological and control process);
12.3. the results of inspections in the work environment
indicate the possible risk of the effect of chemical substances
on employees, it is specified in measurements, that the
occupational exposure limit value (OEV) has been exceeded or
deficiencies of the technological process, equipment or technical
methods have been determined;
12.4. an emergency situation has occurred which has caused or
precipitated an accident, fire, explosion or release of dangerous
chemical substances and mixtures;
12.5. an acute case of occupational poisoning or an
occupational disease caused by a chemical risk factor has been
confirmed; or
12.6. new information regarding the harmfulness of the
relevant chemical substance and mixture to the health of
employees, information regarding the possibility of fire or
explosion, as well as regarding the possibility of the release of
dangerous chemical substances or dangerous mixtures.
[1 February 2011]
13. In the cases referred to in Paragraph 12 of this
Regulation, the employer shall assess the risk caused by changes
and take the necessary preventative measures before assigning
employees to work.
14. The maintenance of equipment and other activities, during
which the safety and health of employees may be endangered and
employees may be exposed to the effects of the chemical
substances and mixtures referred to in Paragraph 2 of this
Regulation, shall also be taken into account in the risk
assessment.
[1 February 2011]
15. The employer shall ensure that the concentration of
chemical substances in the air of the work environment is
regularly determined and compared with the occupational exposure
limit value (OEV), and in accordance with economic and technical
capabilities the employer shall take measures for the reduction
of the actual values of occupational exposure. The employer shall
determine the exposure of chemical substances in the air of the
work environment and assess it in accordance with the methodology
specified in Annex 4 to this Regulation.
16. If the applicable standards have been observed in the
exposure assessment of inhalable chemical substances and
mixtures, it is considered that the requirements for the exposure
assessment of inhalable chemical substances and mixtures at the
workplace are observed.
[1 February 2011]
17. Periodicity for concentration measurements of a chemical
substance shall be determined in accordance with the exposure
index of the chemical substance, which is obtained by dividing
the concentration of the chemical substance (occupational
exposure concentration) in the working environment by the
occupational exposure limit value (OEV):
EI - the exposure index of the chemical substance;
C - the concentration of the chemical substance (occupational
exposure concentration) in the air of the working
environment.
18. If, in determining the concentration of a chemical
substance during one working day or one shift, the exposure index
of the chemical substance is more than 1 (EI > 1), the
exposure in the air of the working environment is larger than the
occupational exposure limit value (OEV). This causes a risk to
the safety and health of an employee and the employer shall
immediately perform measures for risk elimination. After
implementation of the referred to measures the employer shall
perform repeated measurements of the concentration of the
chemical substance in order to ascertain the efficiency of the
measures performed and the reduction of risk up to an admissible
level.
[1 February 2011]
19. If in determining the concentration of a chemical
substance during one working day or one shift the exposure index
of the chemical substance is equal to 0.1 or less (EI ≤ 0,1), the
exposure of the chemical substance in the air of the working
environment is equal to 1/10 of the occupation exposure limit
value (OEV) or less. If it is possible to prove that these levels
are characteristic for the working environment in long term,
periodical measurements shall be optional.
20. The time interval for the next periodical measurement
shall be determined in accordance with the result obtained in the
previous measurements. The maximum time interval up to the next
periodical measurement shall be:
20.1. 104 weeks, if EI ≤ 0.5 in the previous measurements
(occupational exposure concentration is less than a half of the
occupational exposure limit value (OEV));
20.2. 52 weeks, if 0.5 < EI ≤ 0.75 in the previous
measurements (occupational exposure concentration is between a
half and 3/4 of the occupational exposure limit value (OEV));
or
20.3. 24 weeks, if 0.75 < EI ≤ 1 in the previous
measurements (occupational exposure concentration is more than
3/4 or 75 % of the occupational exposure limit value (OEV)).
[1 February 2011]
21. Measurements shall be performed during a working process
(typical working conditions). If working conditions change and a
risk increase has been determined or is possible, additional
measurements of chemical substances shall be carried out.
22. If fast acting chemical substances are discharged in the
air of the working environment, an alarm system shall be
installed for the control of such substances, which notifies
regarding the exceeding of the occupational exposure limit value
(OEV).
23. If employees are exposed to more than one chemical
substance or mixture (simultaneously or gradually), the risk
shall be assessed taking into account the potential mutual and
total exposure of all the chemical substances and mixtures used
at work and the effect thereof on the safety and health of
employees:
23.1. if in the air of the working environment there are
several chemical substances with opposite (antagonistic) effects
concurrently, the occupational exposure limit values (OEVs) shall
remain the same as in case when each substance would affect
separately; or
23.2. if in the air of the working environment there are
several dangerous chemical substances with a similar (synergic)
activity, the total effects of these substances shall be
calculated using the following formula:
| C1 |
+ |
C2 |
+ ········ + |
Cn |
≤ 1, where |
| AER1 |
AER2 |
AERn |
C1; C2; Cn - the
concentration of the substances in the air of the working
environment (mg/m³);
AER1; AER2; AERn - the
occupational exposure limit values of the substances (mg/m³).
The actual concentration ratio of the substances exposure
against OEV (exposure index EI) may not exceed 1 in summing. If
the sum of these fractions is 1, it complies with the limit value
of the total effect.
[1 February 2011]
24. The employer shall document the results of the risk
assessment, including measurement results necessary for the risk
assessment and measures taken for the elimination or reduction of
risk caused by chemical substances and mixtures. Such
documentation shall be kept for at least three years.
[1 February 2011]
25. The employer shall ensure the possibility for employees,
trusted representatives thereof and representatives of employees
to become acquainted with the risk assessment and measurement
results, as well as with the effect of chemical substances and
mixtures on the safety and health of employees.
[1 February 2011]
26. The employer shall ensure accessibility of the risk
assessment results, including measurement results, to a doctor or
an institution responsible for the health care of employees.
27. [1 February 2011]
28. [1 February 2011]
29. [1 February 2011]
III. Prevention and Reduction of
Risk
30. If the type of work and technical capabilities permit
this, the employer shall replace the dangerous chemical
substances and dangerous mixtures with chemical substances and
mixtures that are not dangerous or are less dangerous in the
particular working conditions to the safety and health of
employees.
[1 February 2011]
31. If a risk to the safety and health of employees has been
determined, the employer shall eliminate such risk or, if it is
not possible considering the specific nature of the work, reduce
the risk, taking the following measures:
31.1. equip the workplace with appropriate equipment, as well
as ensure such work organisation, technical methods and
technological processes that do not cause a risk to the safety
and health of employees;
31.2. ensure the regular maintenance of technological
equipment, workplaces and facilities;
31.3. by assigning an employee to work with chemical
substances and mixtures, take into account the professional
education, experience, training and level of preparedness of the
employee in the field of labour protection;
31.4. restrict the number of such employees who work with
chemical substances and mixtures;
31.5. eliminate the contact of employees with chemical
substances and mixtures or reduce to the minimum the duration and
intensity of exposure thereof;
31.6. ensure that only such amount of chemical substances and
mixtures that are necessary for the performance of particular
work is present in work premises; and
31.7. when planning and organising the work process:
31.7.1. ensure correct storage of chemical substances and
mixtures taking into account the compatibility, explosive and
fire safety properties thereof;
31.7.2. separate the place of storage of chemical substances
and mixtures from work premises and equip it with exhaust
ventilation;
31.7.3. eliminate the release of chemical substances, but if
the release has occurred, provide immediate measures for the
liquidation or reduction of the consequences of the release;
31.7.4. classify and mark chemical substances and mixtures, as
well as waste containing such substances or mixtures, ensure safe
and fast collection thereof in accordance with the regulatory
enactments regarding the classification, marking, packaging,
storage, transportation and utilisation of chemical substances
and mixtures, as well as dangerous waste;
31.7.5. demarcate the workplaces appropriately and use safety
signs and notices specified in the regulatory enactments
regarding labour protection requirements for the use of safety
signs;
31.7.6. develop action measures for potential emergency
situations; and
31.7.7. arrange premises appropriate for the rest and
practical needs of employees in which the risk caused by chemical
substances and mixtures has been eliminated.
[1 February 2011]
32. Risk elimination and reduction measures shall be performed
in the following order:
32.1. elimination or maximum reduction of the risk caused by
chemical substances and mixtures at a workplace by establishing
an appropriate system of work processes and technical
supervision;
32.2. utilisation of appropriate work equipment, technologies
and materials, and control of the work environment for the
elimination or reduction of the spreading of dangerous chemical
substances;
32.3. selection and introduction of collective protection
measures directly at the source of the risk (for example, the
general and, if necessary, local exhaust ventilation has been
arranged according to the project and calculations); and
32.4. utilisation of individual labour protection measures,
including personal protection equipment if the effect of chemical
substance and mixture exposure may not be eliminated by the
measures referred to in this Paragraph.
[1 February 2011]
33. If it has been determined that the occupational exposure
limit values (OEV) of chemical substances have been exceeded, the
employer shall immediately take appropriate labour protection
measures.
34. In storing, replacing and separating incompatible chemical
substances and mixtures, the employer shall take into account the
risk caused by the physical, chemical and toxic properties of the
specific chemical substances and mixtures and perform the
following technical and organisational measures for the provision
of safety and health of employees:
34.1. eliminate the accumulation of a dangerous concentration
of highly flammable substances or chemically unstable substances
(substances which under the influence of various external factors
do not retain their properties for a long time) at the workplace
and in the air of the work environment;
34.2. ensure compliance with the fire safety and
explosion-proof regulations and exclude the presence of ignition
sources at workplaces where activities with explosive chemical
substances, mixtures and highly flammable and chemically unstable
substances or mixtures thereof are performed;
34.3. ensure provision of the first aid and other measures
that reduce the effect of harmful factors on the health and
safety of employees if fire or explosion has occurred due to the
ignition of flammable substances or reduce other consequences
caused by chemically unstable substances or mixtures thereof;
and
34.4. ensure compliance with the regulatory enactments in
respect of the safety of equipment and protective systems to be
used in an explosive atmosphere.
[1 February 2011]
35. The employer shall ensure the labelling of packaging,
containers and pipelines of chemical substances and placement of
safety signs at workplaces, and conformity of the labelling with
the contents of the packaging, container or pipeline in
accordance with the regulatory enactments regarding the
procedures for the classification, labelling and packaging and
labour protection requirements for the use of safety signs.
[1 February 2011]
IV. Measures in Emergency
Situations
36. If regulatory enactments regarding the procedures for the
assessment of risk of industrial accidents and measures for risk
reduction are binding on the undertaking, the employer shall
ensure a prior notification in accordance with this
Regulation.
37. If regulatory enactments regarding the procedures for the
assessment of risk of industrial accidents and measures for risk
reduction are not binding on the undertaking, but in carrying out
the assessment of risk it is determined that there is a risk of
accident involving dangerous chemical substances or mixtures, and
it is foreseeable that the consequences of an accident would
affect the territory outside the undertaking, the employer shall
submit the information in writing to the relevant territorial
unit of the State Fire-fighting and Rescue Service, indicating
the chemical substance or the name of the mixture, class of
dangerousness, as well as the relevant risk and safety
phrases.
[1 February 2011]
38. The employer in accordance with the risk assessment shall
develop measures to be taken by employees in case of potential
incidents or accidents at workplaces where work with chemical
substances and mixtures is performed and which are subject to the
risk of an accident, determining the responsible employees and
indicating the procedures on how to contact these employees in an
emergency situation, as well as indicating the telephone numbers
of responsible employees and the State Fire-fighting and Rescue
Service, as well as determining the information to be notified in
case of an accident.
[1 February 2011]
39. Theoretical and practical training of employees regarding
the provision of first aid and action in emergency situations
(for example, fire, release of chemical substances) shall be
organised at least once a year taking into account the specific
nature of the workplace and properties of chemical substances and
mixtures to be used at work.
[1 February 2011]
40. If an emergency situation occurs, the employer shall
immediately inform employees thereof and take measures for the
elimination or reduction of the harmful effects of the chemical
substances and mixtures and the stabilisation of the situation
(for example, disconnection of equipment, evacuation of
employees, containment of fire, leakage control, determination
and demarcation of the danger zone).
[1 February 2011]
41. Only such employees as are involved in repairs or who take
specific measures for the elimination of the emergency situation,
and who are specially trained for such actions, may be present in
the danger zone in emergency situations. Only such repairs or
other work necessary for the elimination or reduction of
consequences and threat caused by the emergency may be performed
in the danger zone in emergency situations.
42. The employer shall provide employees working in the danger
zone with personal protective equipment, specialised safety
equipment and work equipment appropriate for the particular
working conditions. Personal protective equipment, specialised
safety equipment and work equipment shall be used until the
dangerous factors are completely eliminated in accordance with
the risk assessment of such factors and the instructions of the
manufacturer. Persons without appropriate personal protective
equipment are prohibited from being present in the danger zone in
emergency situations.
43. The employer shall ensure efficient operation of alarm and
emergency communication means in order to provide information
immediately to each employee regarding the threats to his or her
safety and health.
44. The employer shall regularly, but at least once a year in
conformity with the risk assessment, revise and update the
measures to be performed in emergency situations, as well as for
the elimination of an emergency situation.
V. Consultation, Information and
Training
45. The employer shall provide employees and trusted
representatives thereof with the training appropriate to the
specific nature of work and necessary information regarding the
relevant labour protection measures so that each employee knows
how to protect himself or herself and other employees at the
workplace. The employer shall ensure the following
information:
45.1. regarding the risk assessment performed in accordance
with the requirements of Chapter II of this Regulation taking
into account any changes at a workplace that may change the risk
assessment data;
45.2. regarding measures for risk elimination and reduction,
and changes in the risk assessment data;
45.3. regarding chemical substances and mixtures in the
workplace, concentration thereof in the air of the work
environment, risk to safety and health of employees, as well as
regarding the occupational exposure limit values (OEV) of
chemical substances and mixtures;
45.4. regarding the characterisation of chemical substances
and mixtures provided for in the safety data sheets in accordance
with Article 31 of Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European
Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 concerning the
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of
Chemicals (REACH), establishing a European Chemicals Agency,
amending Directive 1999/45/EC and repealing Council Regulation
(EEC) No 793/93 and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 as well
as Council Directive 76/769/EEC and Commission Directives
91/155/EEC, 93/67/EEC, 93/105/EC and 2000/21/EC;
45.5. regarding action and measures in emergency
situations.
[1 February 2011; 7 April 2015]
46. The employer shall provide training of such employees who
come or may come into contact with chemical substances or
mixtures:
46.1. prior to the commencement of work;
46.2. regularly, at least once a year; and
46.3. repeatedly if changes which may affect the safety and
health of employees have occurred in the work environment, new
information regarding the properties of the chemical substances
has been received or it has been determined that the level of
knowledge of the employee is not adequate.
[1 February 2011]
47. Employees, trusted representatives of employees and
representatives thereof shall consult and participate in
resolving of the issues provided for in this Regulation in
accordance with the Labour Protection Law.
VI. Special Restrictions and
Prohibitions for the Production, Manufacture and Use of Chemical
Substances and Mixtures at Workplaces, as well as in Performing
Other Activities Therewith
[1 February 2011]
48. Special restrictions that relate to the activities with
individual dangerous chemical substances shall be regulated by
the regulatory enactments regarding restrictions on the
production, trade and use of dangerous chemical substances and
mixtures, except the following cases:
48.1. performance of scientific research, tests and
analysis;
48.2. processing or destruction of chemical substances and
mixtures - by-products or production waste; and
48.3. production and utilisation of chemical substances and
mixtures as intermediate products in a unified, continual
process.
[1 February 2011]
49. In the exception cases specified in Paragraph 48 of this
Regulation it is permitted to perform activities with individual
dangerous chemical substances if the requirements referred to in
Paragraph 50 of this Regulation have been complied with and the
employer has prepared and submitted to the control authorities
the following data prior to the commencement of work:
49.1. justification of the exception;
49.2. calculations on the quantity of chemical substances or
mixtures to be used per year;
49.3. descriptions of such activities (reactions, processes)
during which the relevant chemical substance or mixture is
used;
49.4. the estimated number of employees; and
49.5. the technical and other measures that eliminate or
reduce the risk to the safety and health of employees.
[1 February 2011]
50. The chemical substances and mixtures referred to in
Paragraph 48 of this Regulation may be produced and utilised only
when production and utilisation is performed in a closed system
(a system which does not allow direct contact of an employee with
a chemical substance or mixture) from which chemical substances
are output only if it is necessary for the control of the process
or system maintenance.
[1 February 2011]
VII. Health Surveillance of
Employees
51. Mandatory health examinations shall be performed for
employees who may come into contact with chemical substances and
mixtures at a workplace in accordance with the procedures
specified by regulatory enactments regarding mandatory health
examination. Upon sending an employee to a mandatory health
examination, the employer shall indicate information in the
mandatory health examination card regarding chemical substances,
the type and duration of exposure thereto and the concentration
thereof in the air of the working environment.
[1 February 2011]
52. If an employee comes or may come into contact with
chemical substances or mixtures at the workplace, a competent
specialist or a competent authority and the State Labour
Inspectorate, if necessary, shall have access to the results of
his or her health examination in accordance with the Labour
Protection Law.
[1 February 2011]
53. An employee who comes or may come into contact with
chemical substances or mixtures at the workplace has the right to
become acquainted with the results of the health examination
related thereto.
[1 February 2011]
54. If employees come or may come into contact with chemical
substances and mixtures at the workplace, the results of the
health examination shall be taken into account when developing
labour protection measures at a particular workplace.
[1 February 2011]
55. If it has been determined in a health examination that a
disease or health disorders of employees have been caused due to
the contact with chemical substances or mixtures at the workplace
or the biological limit values (BLV) have been exceeded:
55.1. a doctor of occupational diseases shall inform the
employee regarding the results of the mandatory examination and
provide information and instructions regarding health care also
after termination of the effect of the chemical substances, as
well as in accordance with the regulatory enactments regarding
the procedures for the performance of mandatory health
examinations shall notify the employer regarding non-conforming
conditions of the work environment which may negatively affect
other persons employed in similar conditions, indicating, that
they also are recommended to undergo mandatory health
examinations;
55.2. the employer shall carry out a repeat evaluation of the
risk assessment results and labour protection measures that
eliminate or reduce the relevant risk in conformity with Chapter
III of this Regulation;
55.3. the employer shall consider the recommendations of a
doctor of occupational diseases or occupational health care, a
labour protection specialist, a competent specialist or a
competent authority when taking measures of labour protection for
the elimination or reduction of the risk caused by chemical
substances and mixtures, providing a possibility to assign
employees to alternative work where the risk of exposure to
chemical substances and mixtures does not exist; and
55.4. the employer shall ensure systematic health surveillance
and provide a repeat health examination to any employee who has
been subject to similar exposure of chemical substances or
mixtures.
[1 February 2011]
55.1 The employer shall keep the data of health
examinations referred to in this Chapter for 40 years after the
last known contact of the employee with chemical substances,
afterwards the data shall be handed over to the archives. If the
employer is liquidated, the data of health examinations shall be
kept in accordance with the requirements specified in the
regulatory enactments regarding keeping of archive documents.
[1 February 2011]
VIII. Closing Provisions
[7 January 2020]
56. Cabinet Regulation No. 399 of 3 September 2002, Labour
Protection Requirements when in Contact with Chemical Substances
at Workplaces (Latvijas Vēstnesis, 2005, No. 72) is repealed.
57. The substances referred to in Paragraphs 329.1
and 523 of Annex 1 to this Regulation shall have the following
occupational exposure limit values and transitional periods:
57.1. for hardwood dust - 3 mg/m3 from 17 January
2020 until 17 January 2023;
57.2. for chromium (VI) compounds - 0.010 mg/m3
from 17 January 2020 until 17 January 2025, but for chromium (VI)
compounds in welding or plasma cutting processes or similar work
processes producing vapours - 0.025 mg/m3.
[7 January 2020]
58. Paragraphs 336.1, 528.1, and
603.1 of Annex 1 and Paragraphs 59.1,
236.1, and 311.1 of Annex 2 to this
Regulation shall come into force on 20 May 2021. Amendments to
Paragraphs 72, 231, 275, 336, 388, 429, and 598 of Annex 1 to
this Regulation by which the occupational exposure limit value is
specified and amendments to Annex 2 regarding the deletion of
Paragraphs 306 and 512 shall come into force on 20 May 2021.
[18 February 2021]
59. Paragraphs 77.1, 110.1, and
427.2 of Annex 1 to this Regulation, Paragraph 8 of
the note section of Annex 1, and amendments to Annex 3 shall come
into force on 11 July 2021. The amendment to Paragraphs 271 and
344 of Annex 1 to this Regulation by which the occupational
exposure limit value is specified shall come into force on 11
July 2021. The requirement in relation to the occupational
exposure limit value referred to in Paragraph 77.1 of
Annex 1 to this Regulation for the arsenic acid and its salts as
well as for inorganic arsenic compounds in the field of copper
smelting shall come into force on 11 July 2023.
[18 February 2021]
60. The substances referred to in Paragraphs 110.1,
271, and 344 of Annex 1 to this Regulation shall have the
following occupational exposure limit values and transitional
periods:
60.1. for formaldehyde in the fields of health care, burial,
and embalming - 0.62 mg/m3 or 0.5 ppm until 11 July
2024;
60.2. for beryllium and inorganic beryllium compounds - 0.0006
mg/m3 until 11 July 2026;
60.3. for cadmium and its inorganic compounds - 0.004
mg/m3 until 11 July 2027.
[18 February 2021]
61. The requirement in relation to the occupational exposure
limit value referred to in Paragraph 219.1 of Annex 1
to this Regulation for exhaust emissions from diesel engines
shall come into force on 21 February 2023 but in the field of
underground mining and constructions of tunnels shall come into
force on 21 February 2026.
[18 February 2021 / The abovementioned amendment shall be
included in the wording of the Regulation as of 21 February
2023]
Informative Reference to European
Union Directives
[1 February 2011; 7 April 2015;
10 July 2018; 7 January 2020]
This Regulation contains legal norms arising from:
1) Commission Directive 91/322/EEC of 29 May 1991 on
establishing indicative limit values by implementing Council
Directive 80/1107/EEC on the protection of workers from the risks
related to exposure to chemical, physical and biological agents
at work;
2) Council Directive 98/24/EC of 7 April 1998 on the
protection of the health and safety of workers from the risks
related to chemical agents at work (fourteenth individual
Directive within the meaning of Article 16(1) of Directive
89/391/EEC);
3) Commission Directive 2000/39/EC of 8 June 2000 establishing
a first list of indicative occupational exposure limit values in
implementation of Council Directive 98/24/EC on the protection of
the health and safety of workers from the risks related to
chemical agents at work;
4) Directive 2004/37/EC of the European Parliament and of the
Council of 29 April 2004 on the protection of workers from the
risks related to exposure to carcinogens or mutagens at work
(Sixth individual Directive within the meaning of Article 16(1)
of Council Directive 89/391/EEC);
5) Commission Directive 2006/15/EC of 7 February 2006
establishing a second list of indicative occupational exposure
limit values in implementation of Council Directive 98/24/EC and
amending Directives 91/322/EEC and 2000/39/EC; and
6) Commission Directive 2009/161/EU of 17 December 2009
establishing a third list of indicative occupational exposure
limit values in implementation of Council Directive 98/24/EC and
amending Commission Directive 2000/39/EC;
7) Directive 2014/27/EU of the European Parliament and of the
Council of 26 February 2014 amending Council Directives
92/58/EEC, 92/85/EEC, 94/33/EC, 98/24/EC and Directive 2004/37/EC
of the European Parliament and of the Council, in order to align
them to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 on the classification,
labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures;
8) Commission Directive (EU) 2017/164 of 31 January 2017
establishing a fourth list of indicative occupational exposure
limit values pursuant to Council Directive 98/24/EC, and amending
Commission Directives 91/322/EEC, 2000/39/EC and 2009/161/EU;
9) Directive (EU) 2017/2398 of the European Parliament and of
the Council of 12 December 2017 amending Directive 2004/37/EC on
the protection of workers from the risks related to exposure to
carcinogens or mutagens at work;
10) Directive (EU) 2019/130 of the European Parliament and of
the Council of 16 January 2019 amending Directive 2004/37/EC on
the protection of workers from the risks related to exposure to
carcinogens or mutagens at work;
11) Directive (EU) 2019/983 of the European Parliament and of
the Council of 5 June 2019 amending Directive 2004/37/EC on the
protection of workers from the risks related to exposure to
carcinogens or mutagens at work;
12) Commission Directive (EU) 2019/1831 of 24 October 2019
establishing a fifth list of indicative occupational exposure
limit values pursuant to Council Directive 98/24/EC and amending
Commission Directive 2000/39/EC.
Prime Minister A. Kalvītis
Acting for the Minister for
Welfare,
Minister for the Environment R. Vējonis
In Revised
Version Submitted by the Ministry of Welfare
Annex 1
Cabinet
Regulation No. 325
15 May 2007
Occupational Exposure Limit Values
(OEV) of Chemical Substances in the Air of the Work
Environment
[1 February 2011; 7 April 2015;
10 July 2018; 7 January 2020; 18 February 2021 / Paragraphs
77.1, 110.1, and 427.2 of Annex
and Paragraph 8 of the note section of Annex, and also amendments
to Paragraphs 271 and 344 of Annex by which the occupational
exposure limit value is specified shall come into force on 11
July 2021. The requirement in relation to the occupational
exposure limit value referred to in Paragraph 77.1 of
Annex for the arsenic acid and its salts as well as for inorganic
arsenic compounds in the field of copper smelting shall come into
force on 11 July 2023. The requirement in relation to the
occupational exposure limit value referred to in Paragraph
219.1 of Annex for exhaust emissions from diesel
engines shall come into force on 21 February 2023 but in the
field of underground mining and constructions of tunnels shall
come into force on 21 February 2026 and be included in the
wording of the Regulation as of 21 February 2023. See Paragraphs
59, 60, and 61 of the Regulation]
| No. |
EINECS1 |
CAS2 |
Name of the substance
(including synonyms)
|
Structural formula/sum formula |
Occupational Exposure Limit
Values (OEV) |
Notes |
| |
|
|
|
|
8 h |
Short-term
(15 min.) |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
mg/m³ |
ppm (ml/m3) |
mg/m³ |
ppm (ml/m3) |
|
| 1. |
200-835-2 |
75-05-8 |
Acetonitrile (cyanomethane) |
CH3CN |
70 |
40 |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 2. |
|
75-07-0 |
Acetaldehyde (ethanal) |
CH3CHO |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 3. |
|
50-78-2 |
Acetylsalicylic acid
(2-acetoxybenzoic acid) |
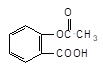 |
0.5 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 4. |
|
98-86-2 |
Acetophenone
(phenyl methyl ketone) |
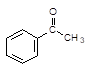 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 5. |
|
75-86-5 |
Acetone cyanohydrin
(?α-hydroxyisobutyronitrile
2-hydroxy-2-methylpropionitrile) |
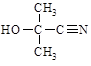 |
0.9 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 6. |
200-662-2 |
67-64-1 |
Acetone
(2-propanol, dimethyl ketone) |
CH3COCH3 |
1210 |
500 |
- |
- |
|
| 7. |
|
124-04-9 |
Adipic acid
(1,4- butanedicarboxylic acid) |
HOOC(CH2)4COOH |
4 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 8. |
|
626-86-8 |
Adipic acid monoethylester
(1,4-butanedicarboxylic acid monoethylester) |
HOOC(CH2)4COOCH2CH3 |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 9. |
|
|
Coal tar and pitch sublimates with average
content of benzopyrene (CAS No. 50-32-8): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* less than 0.075 % |
|
0.2 |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
|
* 0.075-0.15 % |
|
0.1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| |
* 0.15-0.3 % |
|
0.05 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 10. |
201-173-7 |
79-06-1 |
Acrylamide (propenoic acid amide) |
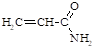 |
0.1 |
- |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 11. |
|
107-13-1 |
Acrylonitrile (cyanoethylene) |
H2C=CH-CN |
0.5 |
- |
- |
- |
Auditory effect |
| 12. |
201-177-9 |
79-10-7 |
Acrylic acid (propenoic acid) propene-2
acid |
H2C=CH-COOH |
5 |
1.7 |
594 |
204 |
|
| 13. |
|
376-84-1 |
Acrylic acid 1H, 1H, 5H-octafluoropenthyl
ester
(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5- octafluoropenthyl acrylate
2-propenoic acid 2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5-octafluoropenthyl
ester) |
H2C=CHCOOCH2
(CF2)5 CF3 |
30 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 14. |
|
103-11-7 |
Acrylic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester
(2-propenoic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester
2-ethylhexyl acrylate) |
H2C=CHCOOCH2
-CH(C2H5)(CH2)3CH3 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 15. |
|
818-61-1 |
Acrylic acid 2-hydroxyethyl ester
(2-hydroxyethyl acrylate) |
H2C=CH-COOCH2CH2OH |
0.5 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 16. |
|
814-68-6 |
Acrylic acid chloroanhydride
(acryloilchloride propenoyl chloride) |
H2C=CH-COCl |
0.3 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 17. |
203-453-4 |
107-02-8 |
Acrolein (acrylaldehyde, 2-propenal) |
H2C=CH-CHO |
0.05 |
0.02 |
0.12 |
0.05 |
|
| 18. |
|
107-95-9 |
β- alanine (3-aminopropanoic acid) |
NH2CH2CH2COOH |
10 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 19. |
203-
470-7 |
107-18-6 |
Allyl alcohol (2-propene-1-ol) |
CH2=CHCH2OH |
4.8 |
2 |
12 1 |
5 |
Skin |
| 20. |
|
21645-51-2 |
Aluminium hydroxide |
Al(OH)3 |
6 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 21. |
|
24304-00-5 |
Aluminium nitride |
AlN |
6 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 22. |
|
1344-28-1 |
Aluminium oxide |
Al2O3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* in the aerosol form of disintegration |
|
6 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| |
|
* in the
mixture with nickel (up to 15 %), (electro-corundum) |
|
4 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 23. |
|
7429-90-5 |
Aluminium and alloys thereof (by
aluminium) |
Al |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 24. |
|
|
Tin inorganic compounds |
after Sn |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 25. |
211-
047-3 |
628-63-7 |
Amyl acetate (pentyl acetate, pentyl
ethanoate) |
CH3COO(CH2)4CH3 |
270 |
50 |
540 |
100 |
- |
| 26. |
|
620-11-1 |
3-Amyl acetate (3-pentyl acetate,
3-pentyl ethanoate) |
CH3COOCH(C2H5)2 |
270 |
50 |
540 |
100 |
- |
| 27. |
|
625-16-1 |
tert-amyl acetate
acetic acid 2-methyl-2-butylester (tert-pentyl
acetate) |
CH3COOC(CH3)2C2H5 |
270 |
50 |
540 |
100 |
- |
| 28. |
|
110-53-2 |
Amyl bromide (pentyl bromide) |
CH3(CH2)4Br |
0.3 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 29. |
|
638-
49-3 |
Amyl formate (pentyl formate,
formic acid pentyl ester) |
HCOOC5H11 |
10 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 30. |
|
71-41-0 |
Amyl alcohol (1-pentanol) |
CH3(CH2)3CH2OH |
10 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 30.1 |
200-521-5 |
61-82-5 |
Amitrole (1,2,4-triazol-3-amine) |
C2H4N4 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 31. |
|
|
Amines, alyphatic (alkyl amines) |
H2N-R, R ≥ C7 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 32. |
|
1918-02-1 |
4-Amino-3,5,6-trichloropicolinic acid
(4-Amino-3,5,6-trichloropyridine-2-carboxylic acid,
tordon-22k, picloram) |
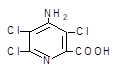 |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 33. |
|
3060-41-1 |
3-Amino-4-phenylbutyric acid
hydrochloride
(phenibute) |
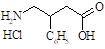 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 34. |
|
6928-85-4 |
1-Amino-4-methylpiperazine
(4-methylpiperazine-1amine) |
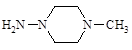 |
2 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 35. |
205-483-3 |
141-43-5 |
2-Aminoethanol (monoethanolamine) |
NH2CH2CH2OH |
0.5 |
0.2 |
7.6 |
3 |
Skin |
| 36. |
|
111-41-1 |
2-(2-Aminoethylamino) ethanol |
NH2CH2CH2NHCH2CH2OH |
3 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 37. |
|
591-27-5 |
3-aminophenol |
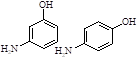 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 38. |
|
123-30-8 |
4-aminophenol |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 39. |
|
929-17-9 |
7-Aminoheptanoic acid |
H2N(CH2)6COOH |
8 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 40. |
|
|
AMINOACIDS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
56-41-7
|
L-alanine
(2-aminopropionic acid
?α-aminopropionic acid) |
CH3CH(NH2)COOH |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 41. |
|
74-79-3 |
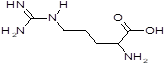
Arginine
(2-amino-5-guanidinovaleric acid) |
 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 42. |
|
56-84-8 |
Aspartic acid
(2-aminosuccinic acid) |
HOOCCH2CH(NH2)COOH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 43. |
|
52-90-4 |
Cysteine
(2- amino -3-mercaptopropanoic acid,
α - amino- β -mercaptopropionic acid) |
HSCH2CH(NH2)COOH |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 44. |
|
56-89-3
|
Cystine
(3,3'-Dithiobis-2-aminopropanoic acid,
2-amino-3-(2-amino-2-carboxyethyldisulfanyl)
propanoic acid) |
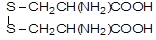 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 45. |
|
63-91-2
|
Phenylalanine
(2-amino-3-phenyl-propanoic acid,
α - amino- β -phenylpropionic acid) |
C6H5-CH2
CH(NH2)COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 46. |
|
56-40-6
|
Glycine (aminoacetic acid) |
NH2CH2COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 47. |
|
56-86-0
|
Glutamic acid
(1-amino-propane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid) |
HOOCCH2CH2CH(NH2)COOH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 48. |
|
71-00-1
|
Histidine
(2-amino-3-(4-imidazolyl)propanoic acid) |
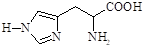 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 49. |
|
73-32-5
|
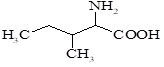
Isoleucine
(2-amino-3-methyl-pentanoic acid
α-amino- β -methylvaleric acid) |
 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 50. |
|
61-90-5 |
Leucine
(2-amino-4-methyl-pentanoic acid,
α - aminoisocaproic acid) |
(CH3)2CHCH2CH(NH2)COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 51. |
|
56-87-1 |
Lysine
2,6-diaminohexanoic acid,?
α, ε diaminocaproic acid |
NH2(CH2)4CH(NH2)COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 52. |
|
63-68-3 |
Methionine
(2-amino-4-methylmercaptobutyric acid,
α - amino-g-methylthiobutyric acid) |
CH3SCH2CH2CH(NH2)COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 53. |
|
98-79-3 |
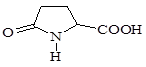
5-Oxoproline
(glutamic acid 5-lactam
pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic acid) |
 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 54. |
|
147-85-3 |
Proline
(2-pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid) |
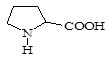 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 55. |
|
56-45-1 |
Serine
(2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid) |
HOCH2CH(NH2)COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 56. |
|
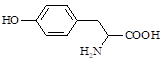
60-18-4 |
Tyrosine
(2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-propanoic acid,
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)alanine) |
 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 57. |
|
72-19-5 |
Threonine
(2-amino-3-hydroxy-butanoic acid) |
CH3CH(OH)CH(NH2)COOH |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 58. |
|
73-22-3 |
Tryptophan
(2-amino-3-(3-indolyl)propanoic acid) |
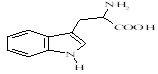 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 59. |
|
72-18-4 |
Valine
(2-amino-3-methyl-butanoic acid) |
(CH3)2CHCH(NH2)COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 60. |
|
7783-28-0 |
Ammophos
(ammonium hydrogen phosphate and dihydrogen phosphate
mixture, diammonium hydrogen orthophosphate) |
NH4H2PO4,
(NH4)2HPO4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 61. |
|
16919-58-7 |
Ammonium (IV)hexachloroplatinate |
(NH4)2[PtCl6] |
0.005 |
|
|
|
|
| 62. |
|
1309-32-6 |
Ammonium hexafluorosilicate (after
fluorine) |
NH4SiF6 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 63. |
|
12125-02-9 |
Ammonium chloride |
NH4Cl |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 64. |
|
1762-95-4 |
Ammonium rodanide
(ammonium thiocyanate) |
NH4SCN |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 65. |
213-695-2 |
1002-89-7 |
Ammonium stearate |
[CH3(CH2)16COO]NH4 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 66. |
|
7773-06-0 |
Ammonium sulfamate |
NH4SO3NH2 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 67. |
|
7783-18-8 |
Ammonium thiosulphate |
(NH4)2S2O3 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 68. |
231-635-3 |
7664-41-7 |
Ammonia |
NH3 |
14 |
20 |
36 |
50 |
|
| 69. |
|
69-53-4 |
Ampicillin
(adobacillin,
Aminophenylmethyl-penicillin,
aminobenzylpenicillin) |
C16H20N3O4S |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 70. |
|
5907-38-0 |
Analgine
(sodium
[(2-phenyl-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methyl-amino]methanesulfonate) |
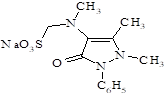 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 71. |
|
|
Anaesthetic gases
(halothane, sevoflurane, isoflurane, enflurane, desflurane,
and other haloalkanes) |
|
20 |
2 |
|
|
|
| 72. |
200-539-3 |
62-53-3 |
Aniline
(aminobenzene, phenylamine) |
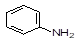 |
7.74 |
2 |
19.35 |
5 |
Skin |
| 73. |
|
104-94-9 |
Anisidine (p-anisidine;
4-amino-1-methoxybenzene, 4-methoxyaniline) |
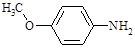 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 74. |
|
7440-36-0 |
Antimony metallic dust |
Sb |
0.2 |
|
0.5 |
|
|
| 75. |
|
1309-64-4 |
Antimony trioxide
(recalculating into antimony) |
Sb2O3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 76. |
215-237-7 |
1314-60-9 |
Antimony pentoxide
(recalculating into antimony) |
Sb2O5 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 77. |
|
|
Arsenic inorganic compounds (after
arsenic) |
(As) |
0.01 |
|
0.04 |
|
|
| 77.1 |
|
|
Arsenic acid and its salts as well as
inorganic arsenic compounds |
|
0.015 |
|
|
|
|
| 78. |
|
12001-29-5 |
Asbestos |
3 MgOx2 SiO2x2
H2O |
0,1 sol. /cm3 air |
|
|
|
|
| 79. |
|
109-52-4 |
Valeric acid
(pentanoic acid) |
CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 80. |
|
12253-23-5 |
Barium aluminate |
BaAl2O4 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 81. |
|
|
Barium aluminosilicate |
BaAl2Si2O8 |
0.5 |
|
1 |
|
|
| 82. |
|
52869-91-7 |
Aluminum barium titanate |
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 83. |
|
23436-05-7 |
Barium borate
(orthoboric acid barium salt) |
Ba3(BO3)2 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 84. |
|
13718-55-3 |
Barium chloride fluoride (luminophores P -
385) |
BaClF |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 85. |
|
7787-32-8 |
Barium fluoride |
BaF2 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 86. |
|
10048-98-3 |
Barium hydrogenorthophosphate
(barium hydrogen phosphate) |
BaHPO4 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 87. |
|
52869-93-9 |
Barium calcium titanate |
BaCaTi2O6 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 88. |
|
513-77-9 |
Barium carbonate |
BaCO3 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 89. |
|
13462-86-7 |
Barium sulfate (barite) |
BaSO4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 90. |
|
|
Barium soluble compounds |
after Ba |
0.5 |
|
|
|
Skin |
| 91. |
|
125693-49-4 |
Barium tetratitanate |
BaTi4O9 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 92. |
|
12047-27-7 |
Barium titanate (IV) |
BaTiO3 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 93. |
|
103-83-3 |
Benzyldimethylamine |
C6H5CH2N(CH3)2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 94. |
|
50-32-8 |
Benz(a)pyrene
(benzo[def]chrysene) |
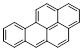 |
0.00015 |
|
|
|
|
| 95. |
|
100-52-7 |
Benzaldehyde |
C6H5CHO |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 96. |
|
140-11-4 |
Benzyl acetate (acetic acid, benzyl
ester) |
CH3COOCH2C6H5 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 97. |
|
100-44-7 |
Benzyl chloride (α-chlorotoluene) |
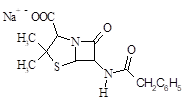
C6H5CH2Cl |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 98. |
|
98-87-3 |
Benzylidene chloride
(α,α-dichlorotoluene, benzal chloride,
dichloromethylbenzene) |
C6H5CHCl2 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 99. |
|
69-57-8 |
Benzylpenicillin
(6-phenylacetamido penicillinic acid sodium salt) |
 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 100. |
|
100-51-6 |
Benzyl alcohol
(phenylmethanol, phenylcarbinol) |
C6H5CH2OH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 101. |
|
8030-30-6 |
Petroleum spirits (fuel) |
|
100 |
|
|
|
|
| 102. |
|
106-51-4 |
1,4- benzoquinone
(p- benzoquinone) |
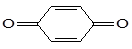 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 103. |
|
98-88-4 |
Benzoyl chloride
(benzoic acid chloroanhydride) |
C6H5COCl |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 104. |
200-753-7 |
71-43-2 |
Benzene |
C6H6 |
3.25 |
1 |
|
|
Skin |
| 105. |
|
528-44-9 |
1,2,4-benzenetricarboxylic acid
(trimellitic acid) |
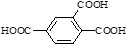 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 106. |
|
100-47-0 |
Benzonitrile (cyanobenzene) |
C6H5CN |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 107. |
|
65-85-0 |
Benzoic acid |
C6H5COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 108. |
|
87-25-2 |
Benzoic acid 2-amino- ethyl ester
(ethyl 2-aminobenzoate) |
C6H5COOCH2CH2NH2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 109. |
|
95-14-7 |
Benzotriazole |
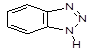 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 110. |
|
7440-41-7 |
Beryllium and its compounds |
After Be |
0.001 |
|
|
|
|
| 110.1 |
|
|
Beryllium and inorganic beryllium
compounds |
|
0.00025 |
|
|
|
Substance may cause skin or respiratory
sensitisation |
| 111. |
|
13684-63-4 |
Betanal
(phenmedipham,
1-pyridylacetic acid betaine,
1-carboxymethyl pyridinium betaine) |
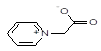 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 112. |
|
92-52-4 |
Biphenyl (diphenyl) |
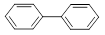 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 113. |
|
366-18-7
and
553-26-4 |
2,2'- bipyridyl and 4,4'-bipyridyl
2,2'-bipyridine and 4,4'-bipyridine,
2,2'-dipyridyl and 4,4'-dipyridyl) |
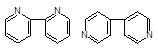 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 114. |
|
7440-69-9 |
Bismuth and its inorganic compounds |
After Bi |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 115. |
|
12069-32-8 |
Boron carbide |
B4C |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 116. |
|
10043-11-5 |
Boron nitride |
BN |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 117. |
|
7637-07-2 |
Boron fluoride (boron trifluoride) |
BF3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 118. |
|
10043-35-3 |
Boric acid |
H3BO3 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 119. |
|
63428-82-0 |
Boverin (mixture of isomers) |
|
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 120. |
231-778-1 |
7726-95-6 |
Bromine |
Br2 |
0.7 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
| 121. |
|
353-59-3
|
Bromochlorodifluoromethane
(freon 12Br
difluorochlorobromomethane) |
CBrClF2 |
1000 |
|
|
|
|
| 121.1 |
209-800-6 |
593-60-2 |
Bromoethylene |
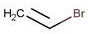 |
4.4 |
1 |
|
|
|
| 122. |
|
95-56-7
and
106-41-2 |
Bromophenol, o- and p-isomers |
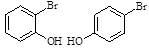 |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 123. |
|
107-81-3 |
2-bromopentane |
CH3CHBrCH2CH2CH3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 124. |
|
75-63-8 |
Bromotrifluoromethane
(trifluorobromomethane,
freon 13 B1) |
F3BrC |
3000 |
|
|
|
|
| 125. |
233-113-0 |
10035-10-6 |
Hydrobromic acid |
HBr |
- |
- |
6.7 |
2 |
- |
| 126. |
201-159-0 |
78-93-3 |
2-Butanone
(methylethylketone,
ethylmethylketone) |
CH3CH2COCH3 |
200 |
67 |
900 |
300 |
- |
| 127. |
203-450-8 |
106-
99-0 |
1,3-butadiene |
CH2=CH-CH=CH2 |
2.2 |
1 |
|
|
|
| 127.1 |
203-788-6 |
110-65-6 |
But-2-yn 1,4-diol (1,4-butynediol) |
C4H6O2/OHCH2CCCH2OH |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 128. |
|
106-97-8 |
Butane |
CH3CH2CH2CH3 |
300 |
|
|
|
|
| 129. |
205-480-7 |
141-32-2 |
n-Butyl acrylate |
CH2=CHCOO(CH2)3CH3 |
11 |
2 |
53 |
10 |
- |
| 130. |
|
109-73-9 |
Butylamine |
CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 131. |
|
109-65-9
|
Butyl bromide (1-bromobutane) |
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 132. |
|
75-91-2 |
tert-Butyl hydroperoxide |
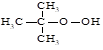 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 133. |
|
109-69-3
|
Butyl chloride (1-chlorobutane) |
CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 134. |
|
111-36-4 |
Butyl isocyanate |
CH3CH2CH2CH2N=C=O |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 135. |
|
97-88-1
|
Butyl methacrylate
(2-propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, butyl ester) |
CH2=C(CH3)COOC4H9 |
30 |
|
|
|
|
| 136. |
|
628-28-4 |
Butyl methyl ether |
CH3OC4H9 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
| 137. |
|
|
Butyl alcohol (primary, secondary,
tertiary) |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
71-36-3 |
(n-butanol, |
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1-butanol, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
78-92-2 |
2-butanol, |
CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75-65-0 |
2-methyl-propan-2-ol, |
(CH3)3COH |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tert-butanol, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
78-83-1 |
2-methyl-propan-1-ol, |
(CH3)2CHCH2OH |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
iso-butyl alcohol) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 138. |
|
111-34-2 |
Butyl vinyl ether |
CH2=CHOC4H9 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
| 139. |
203-905-0 |
111-76-2 |
2-butoxyethanol,
(ethyleneglycol monobutyl ether,
Butyl cellosolve) |
HOCH2-CH2-O-C4H9 |
98 |
20 |
246 |
50 |
Skin |
| 140. |
203-933-3 |
112-07-2 |
2-butoxyethyl acetate (ethyleneglycol
monobutyl ether acetate,butyl glycol acetate) |
CH3COOCH2CH2O(CH2)3CH3 |
133 |
20 |
333 |
50 |
Skin |
| 141. |
203-961-6 |
112-34-5 |
2-(2-butoxyethoxy)ethanol (butyl
diglycol) |
HOC2H4OCH2CH2O(CH2)3CH3 |
67.5 |
10 |
101.2 |
15 |
|
| 142. |
|
61-24-5
525-94-0
28393-42-2
|
Cephalosporin C;
Penicillin N (cephalosporin N); cephalosporin P; |
C16H21N3O8S
C14H21N3O6S
C33H50O8
|
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 143. |
|
9004-34-6 |
Wood pulp |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 144. |
|
65997-15-1 |
Cement (Portland cement) |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 145. |
|
7758-88-5 |
Cerium (III) fluoride |
CeF3 |
0.5 |
|
2.5 |
|
|
| 146. |
|
1306-38-3 |
Cerium dioxide |
CeO2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 147. |
|
21351-79-1 |
Caesium hydroxide |
CsOH |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 148. |
206-992-3 |
420-04-2 |
Cyanamide (carbamonitrile) |
H2NCN |
1 |
0.58 |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 149. |
200-821-6 |
74-90-8 |
Hydrogen cyanide (hydrocyanic acid) |
HCN |
0.3 |
0.27 |
5 |
4.5 |
Skin |
| 150. |
203-631-1 |
108-94-1 |
Cyclohexanone |
 |
40.8 |
10 |
81.6 |
20 |
Skin |
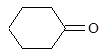
| 151. |
|
100-64-1 |
Cyclohexanone oxime |
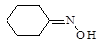 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 152. |
203-806-2 |
110-82-7 |
Cyclohexane |
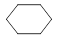 |
80 |
23 |
|
|
|
| 153. |
|
108-91-8 |
Cyclohexylamine |
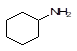 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 154. |
|
|
Cymol (2,3,4- mixture of isomers or separate
isomers)
(2-isopropyltoluene
o-cymol
3-isopropyltoluene
m-cymol
4-isopropyltoluene
p-cymol) |
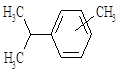 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 155. |
|
12122-67-7 |
Zincethylene-N,N'-bisdithiocarbamate
(N,N'-ethanediylbis-dithiocarbamic acid zinc salt,
zineb, cuprozan) |
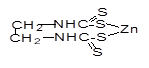 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 156. |
|
1314-84-7 |
Zinc phosphide (trizinc diphosphide) |
Zn3P2 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 157. |
|
10192-46-8 |
Zinc hexaborate
(diboron trizinc hexaoxide) |
Zn2B6O11 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 158. |
|
1314-13-2 |
Zinc oxide |
ZnO |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 159. |
|
1314-98-3 |
Zinc sulphide |
ZnS |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 160. |
|
112-30-1
|
n-Decyl alcohol (1-decanol) |
CH3(CH2)8CH2OH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 160.1 |
207-069-8 |
431-03-8 |
Diacetyl (butanedione, dimethyl
diketone) |
CH3COCOCH3 |
0.07 |
0.02 |
0.36 |
0.1 |
|
| 161. |
|
131-17-9 |
Diallyl phthalate
(1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, di-2-propenyl ester) |
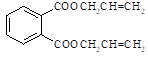 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 162. |
|
83968-18-7 |
Dialkylphthalate
(1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, dialkyl esters) |
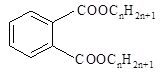 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 163. |
|
2687-25-4 |
2,3 Diaminotoluene
(toluene-2,3- diamine) |
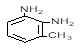 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 164. |
|
1303-86-2 |
Diboron trioxide |
B2O3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 165. |
|
105-99-7 |
Dibutyl adipinate
(adipic acid dibutyl ester,
hexanedioic acid dibutyl ester,
1,4-butane dicarbonic acid dibutyl ester) |
C4H9OOC(CH2)4COOC4H9 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 166. |
|
2528-36-1 |
Dibutyl phenylphosphate
(phosphoric acid, dibutyl phenyl ester) |
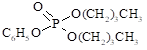 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 167. |
|
84-74-2
|
Dibutyl phthalate
DBP,
1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid dibutyl ester) |
C6H4(COOC4H9)2 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 168. |
|
502-56-7 |
Dibutyl ketone |
CH3(CH2)3CO(CH2)3CH3 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
| 169. |
|
109-43-3 |
Dibutyl sebacinate
(sebacic acid dibutyl ester,
decanedioic acid dibutyl ester) |
C4H9OOC(CH2)8COOC4H9 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 170. |
203-716-3 |
109-89-7 |
Diethylamine |
(C2H5)2
NH |
15 |
5 |
30 |
10 |
- |
| 171. |
|
111-46-6 |
Diethylene glycol
2,2'-oxybisethanol,
2,2'-dihydroxydiethyl ether) |
HOCH2CH2-O-CH2CH2OH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 172. |
200-467-2 |
60-29-7 |
Diethyl ether |
C2H5-O-C2H5 |
308 |
100 |
616 |
200 |
- |
| 173. |
|
84-66-2 |
Diethyl phthalate
(1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, diethyl ether) |
C6H4(COOC2H5)2 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 174. |
|
82-66-6 |
Diphenacin
(diphenylacetyl-1,3-Indandion,
ratindan, diphacinone) |
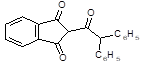 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
| 175. |
|
|
Diphenyls, chlorinated |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 175.1 |
202-981-2 |
101-84-8 |
Diphenyl ether (phenylene ether,
phenoxybenzene) |
C6H5OC6H5 |
7 |
1 |
14 |
2 |
|
| 176. |
|
76-12-0
|
1,2-Difluoro-1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane
(tetrachlorodifluoroethane,
freon -112) |
Cl2FC-CFCl2 |
1000 |
|
|
|
|
| 177. |
|
75-71-8 |
Dichloro-difluoro-methane
(Freon 12) |
CCl2F2 |
3000 |
|
|
|
|
| 178. |
|
624-72-6 |
1,2-Difluoroethane, (Freon 152) |
FH2C-CH2F |
3000 |
|
|
|
|
| 179. |
|
25497-29-4
|
1,2-Difluorochloroethane
(Freon 142) |
FH2C-CHClF |
3000 |
|
|
|
|
| 180. |
200-871-9 |
75-45-6 |
Difluorochloromethane |
CHClF2 |
3600 |
1000 |
- |
- |
|
| 181. |
|
886-77-1 |
Difurfurylideneacetone |
 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 182. |
202-425-9 |
95-50-1 |
1,2-Dichlorobenzene,
(o-dichlorobenzol) |
C6H4Cl2 |
122 |
20 |
306 |
50 |
Skin |
| 183. |
|
541-73-1 |
1,3-Dichlorobenzene
(m-dichlorobenzol) |
Cl2C6H4 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
| 184. |
203-400-5 |
106-46-7 |
1,4-dichlorobenzene,
(p-dichlorobenzene) |
C6H4Cl2 |
12 |
2 |
60 |
10 |
Skin |
| 185. |
200-863-5 |
75-34-3 |
1,1-dichloroethane |
CH3CHCl2 |
412 |
100 |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 186. |
203-458-1 |
107-06-2 |
1,2-dichloroethane (ethylene
dichloride) |
C2H4Cl2 |
8.2 |
2 |
|
|
Skin |
| 187. |
|
79-43-6 |
Dichloroacetic acid |
Cl2CHCOOH |
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 188. |
|
102-36-3 |
3,4-Dichlorophenyl isocyanate |
 |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 189. |
|
149-74-6 |
Dichloro-phenyl-methyl-silane (after
HCL) |
C6H5SiCl2CH3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 190. |
|
27137-85-5 |
2,5-Dichlorophenyltri-chlorosilane |
Cl2C6H3-SiCl3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 191. |
|
84-69-5 |
Diisobutyl phthalate
(1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, diisobutylester) |
C6H4(COOC4H9)2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 192. |
204-697-4 |
124-40-3 |
Dimethylamine |
(CH3)2NH |
3.8 |
2 |
9, 4 |
5 |
- |
| 193. |
|
1149-23-1 |
2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid
diethyl ester
(2,6-dimethyl-3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydropyridine,
diludine,
diethyl
1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate) |
 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 194. |
204-826-4 |
127-19-5 |
N,N-Dimethylacetamide |
CH3CON(CH3)2 |
36 |
10 |
72 |
20 |
Skin |
| 195. |
|
108-01-0
|
2-(Dimethylamino) ethanol
(N,N-dimethyl-2-hydroxyethylamine,
N,N-dimethylethanolamine) |
(CH3)2NCH2CH2OH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 196. |
|
121-69-7
|
N,N-Dimethylaniline
(N,N-dimethylphenylamine) |
(CH3)2N-C6H5 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 197. |
|
103-83-3 |
N,N-Dimethylbenzylamine |
C6H5CH2N(CH3)2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 198. |
|
80-15-9 |
α α Dimethylbenzylhydroperoxide
(Cumolhydroperoxide) |
C9H12O2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 199. |
204-065-8 |
115-10-6 |
Dimethyl ether |
CH3-O-CH3 |
1920 |
1000 |
- |
- |
- |
| 200. |
|
576-26-1
|
2,6-Dimethylphenol (2,6-Xylenol) |
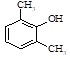 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 201. |
|
68-12-2 |
N,N-dimethylformamide |
HCON(CH3)2 |
15 |
5 |
30 |
10 |
Skin |
| 202. |
|
131-11-3
|
Dimethyl phthalate
(1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, dimethyl ester) |
C6H4(COOCH3)2 |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 203. |
|
106-79-6
|
Dimethyl sebacate
(1,8-octanedicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester,
decanedioic acid dimethyl ester,
sebacic acid, dimethyl ester) |
CH3OOC(CH2)8COOCH3 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 204. |
|
77-78-1 |
Dimethyl sulphate |
(CH3)2SO4 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 205. |
|
75-18-3 |
Dimethyl sulphide |
H3C-S-CH3 |
50 |
|
|
|
|
| 206. |
|
120-61-6 |
Dimethyl terephthalate
(1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid, dimethyl ester) |
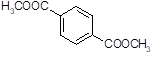 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 207. |
|
110-71-4 |
1,2-dimethoxyethane
(ethylene glycol dimethyl ether) |
CH3OCH2CH2OCH3 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 208. |
203-714-2 |
109-87-5
|
Dimethoxymethane (formaldehyde dimethylacetal,
methylal) |
CH3OCH2OCH3 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 209. |
|
528-29-0 |
1,2-dinitrobenzene |
C6H4(NO2)2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 210. |
|
99-65-0 |
1,3-dinitrobenzene |
C6H4(NO2)2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 211. |
|
100-25-4 |
1,4-dinitrobenzene |
C6H4(NO2)2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 212. |
|
25550-58-7 |
2,4-dinitrophenol |
 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 213. |
|
27478-34-8 |
Dinitronaphthalene (mixture of 1,5- and 1,8-
isomers) |
C10H6(NO2)2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 214. |
|
121-14
-2,
606-20-2,
610 -39-9 |
Dinitrotoluene (2, 4- and 2,6- and
3,4-isomers) |
(NO2)2C6H3CH3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 215. |
|
84-76-4
|
Dinonylphthalate
(1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, dinonyl ester) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 216. |
|
123-91-1 |
1,4-dioxane |
 |
20 |
5.5 |
|
|
|
| 217. |
|
122-62-3
|
Dioctyl sebacate
(octan-1,8-dicarboxilic acid dioctyl ester,
sebacic acid dioctyl ester,
bis(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate) |
C8H17OOC(CH2)8COOC8H17 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 218. |
|
142-84-7 |
Dipropylamine |
(CH3CH2CH2)2NH |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 219. |
|
1335-47-3 |
Ditolylmethane |
(CH3C6H4)2CH2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 220. |
|
112-53-8
|
Dodecyl alcohol
(dodecan-1-ol, lauryl alcohol) |
CH3(CH2)10CH2OH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 221. |
|
25991-86-0
|
dodecahydr-1,1'-
carbonyl-bis-1H-azepin
bis-azepan-1-ylmethanone,
bis-N,N'-hexamethylene urea,
carboxide (pesticide)) |
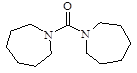 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 222. |
|
13463-40-6
|
Iron pentacarbonyl (pentacarbonyliron) |
Fe(CO)5 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 223. |
|
|
Iron ore (iron agglomerate) |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 224. |
|
7439-97-6 |
Mercury and its inorganic compounds (after
mercury) |
Hg |
0.02 |
|
|
|
Auditory effect |
| 224.1 |
|
21908-53-2 |
Mercuric oxide (after mercury) |
HgO |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 224.2 |
|
7487-94-7 |
Mercuric chloride (after mercury) |
HgCl2 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 225. |
|
107-15-3 +
58-55-9
|
Elixophylline
(theophylline + 1,2 ethylenediamine) |
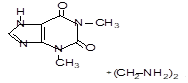 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 226. |
203-439-8 |
106-89-8
|
Epichlorohydrin
(3-chloro-1,2-epoxypropane,
1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane) |
C3H5ClO |
1.9 |
|
|
|
Skin |
| 227. |
|
|
Epoxide resins (after epichlorohydrin) |
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 228. |
|
75-08-1
|
Ethanethiol (ethyl mercaptan) |
C2H5SH |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 229. |
|
94-19-9 |
Etazole
amino-N-(5-ethyl-[1,3,4]thiadiazol-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide,
sulfaethidiole, sulfaethylthiadiazole) |
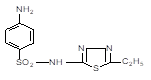 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 230. |
|
108-24-7 |
Acetic acid anhydride |
CH3CO-O-COCH3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 231. |
204-658-1 |
123-86-4
|
Acetic acid butyl ester
(n-butyl acetate) |
CH3COOC4H9 |
241 |
50 |
723 |
150 |
|
| 232. |
205-500-4 |
141-78-6 |
Acetic acid ethyl ester (ethyl acetate) |
CH3COOC2H5 |
200 |
54 |
1468 |
400 |
|
| 233. |
|
140-88-5
|
Ethyl acrylate (2-propenoic acid ethyl
ester, acrylic acid ethyl ester) |
H2C=CH-COOC2H5 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 234. |
200-
834-7 |
75-04-7 |
Ethylamine |
C2H5NH2 |
9.4 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
| 235. |
202-849-4 |
100-41-4 |
Ethylbenzene |
C6H5C2H5 |
442 |
100 |
884 |
200 |
Skin;
Auditory effect
|
| 236. |
|
74-96-4 |
Ethyl bromide (bromoethane) |
CH3CH2Br |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 237. |
|
110-80-5 |
Ethyl cellosolve
(ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, 2-ethoxyethanol) |
C2H5-O-CH2CH2OH |
8 |
2 |
|
|
Skin |
| 238. |
|
107-15-3 |
Ethylenediamine
(1,2-diaminoethane) |
NH2CH2CH2NH2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 238.1 |
203-444-5 |
106-93-4 |
Ethylene dibromide |
C2H4Br2 |
0.8 |
0.1 |
|
|
Skin |
| 239. |
203-473-3 |
107-21-1 |
Ethylene glycol,
(1,2-ethanediol) |
HOCH2-CH2OH |
52 |
20 |
104 |
40 |
Skin |
| 240. |
|
818-61-1 |
Ethyleneglycol monoacrylester
(propenoic acid 2-hydroxyethyl ester) |
CH2=CHCOOCH2CH2OH |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 241. |
|
151-56-4 |
Ethyleneimine (aizirdine) |
 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 242. |
200-849-9 |
75-21-8 |
Ethylene oxide (oxirane) |
 |
1 |
0.55 |
|
|
Skin |
| 243. |
|
74-85-1 |
Ethylene |
CH2=CH2 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
| 243.1 |
203-234-3 |
104-76-7 |
2-ethylhexan-1-ol (2-Ethyl-1-hexanol,
2-ethylhexyl alcohol) |
CH3(CH2)3CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH |
5.4 |
1 |
|
|
|
| 244. |
200-830-5 |
75-00-3 |
Ethyl chloride (chloroethane) |
CH3CH2Cl |
50 |
19 |
268 |
105 |
|
| 245. |
|
|
N-butyl-N-ethyl-S-propylthiocarbamate
(tillam) |
(C2H5)N(C4H9)C(O)SC3H7 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 246. |
|
64-17-5 |
Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) |
C2H5OH |
1000 |
|
|
|
|
| 247. |
200-580-7 |
64-19-7 |
Acetic acid (ethanoic acid) |
CH3COOH |
25 |
10 |
50 |
20 |
|
| 247.1 |
|
111-15-9 |
2-ethoxyethyl acetate |
C6H12O3 |
11 |
2 |
|
|
Skin |
| 248. |
|
106-74-1 |
2-ethoxyethyl acrylate
(acrylic acid 2-ethoxyethyl ester
2-propenoic acid 2-ethoxyethyl ester) |
CH2=CHCOOCH2CH2OC2H5 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 249. |
|
85-01-08 |
Phenanthrene |
 |
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
| 250. |
202-705-0 |
98-83-9 |
2-phenylpropene (isopropylbenzene,
α-methylstyrene) |
C6H5C(CH3)=CH2 |
246 |
50 |
492 |
100 |
- |
| 251. |
|
80-15-9 |
2-phenyl-2-propylhydroperoxide
(cumene hydroperoxide, cumyl hydroperoxide,
isopropylbenzene hydroperoxide,
α,α-dimethylbenzyl hydroperoxide) |
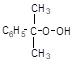 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 252. |
|
58-15-1 |
2-phenyl-4-dimethylamino-1,5-dimethyl-1,2-dihydropyrazol-3-one
(amidopyrin, piramidon) |
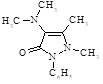 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 253. |
|
140-29-4 |
Phenylacetonitrile (benzyl cyanide) |
C6H5CH2CN |
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
| 254. |
|
6017-21-6 |
Phenylazomalondinitrile
(2-phenylazomalononitrile,
Phenylhydrazonomalononitrile) |
C6H5-N=NCH(CN)2 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 255. |
|
108-45-2 |
m-Phenylene diamine
(1,3-phenylenediamine) |
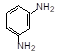 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 256. |
|
95-54-5 |
o-phenylenediamine
(1,2-phenylenediamine) |
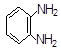 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 257. |
|
106-50-3 |
p-phenylenediamine
(1,4-phenylenediamine) |
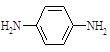 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 258. |
|
3006-93-7 |
N, N'-1,3-Phenylenedimaleimide
(N,N'-(m-phenylene) disuccinimide,
1,1'-(1,3-Phenylene)bis(1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione)) |
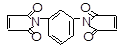 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 259. |
|
103-71-9 |
Phenyl isocyanate |
C6H5N=C=O |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 260. |
|
1007-36-9 |
N-Phenyl-N'-methylurea |
C6H5NHCONHCH3 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 261. |
|
122-59-8 |
Phenoxyacetic acid |
C6H5OCH2COOH |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 262. |
|
713-68-8 |
m-Phenoxyphenol (3-Phenoxyphenol) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 263. |
[1 February 2011] |
| 264. |
203-632-7 |
108-95-2 |
Phenol (hydroxybenzene) |
C6H5OH |
8 |
2 |
16 |
4 |
Skin |
| 265. |
|
|
Fluorides, inorganic |
By F |
2.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 266. |
231-954-8 |
7782-41-4 |
Fluorine |
F2 |
1.58 |
1 |
3.16 |
2 |
- |
| 267. |
|
430-57-9 |
1-Fluorine-1,2-dichloroethane
(1,2-dichlorofluoro-ethane, freon 141) |
HClFC-CClH2 |
1000 |
|
|
|
|
| 268. |
|
75-69-4 |
Trichloro-fluoro-methane
(Freon 11) |
Cl3FC |
1000 |
|
|
|
|
| 269. |
231-634-8 |
7664-39-3 |
Hydrogen fluoride |
HF |
1.5 |
1.8 |
2.5 |
3 |
- |
| 270. |
|
|
Hydrofluoric acid salts (after F): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* tin, ammonium, barium, zinc, potassium, lithium ,
sodium, silver fluorides, ammonium, hydrofluoride, trisodium
hexafluoroaluminate,
|
|
0.2 |
|
1 |
|
|
* aluminum, chrome, magnesium, calcium, strontium,
copper
|
|
0.5 |
|
2.5 |
|
| 271. |
200-001-8 |
50-00-0
|
Formaldehyde (methanal) |
HCHO |
0.37 |
0.3 |
0.74 |
0.6 |
Substance may cause skin sensitisation |
| 272. |
232-260-8 |
7803-51-2 |
Phosphine |
PH3 |
0.14 |
0.1 |
0.28 |
0.2 |
|
| 273. |
233-060-3 |
10026-13-8 |
Phosphorus (V) chloride
(phosphorus pentachloride) |
PCl5 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 274. |
215-236-1 |
1314-56-3 |
Phosphorus (V) oxide,
(diphosphorus pentaoxide,
phosphorus pentaoxide) |
P2O5 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 275. |
233-046-7 |
10025-87-3 |
Phosphorus oxychloride
(phosphoryl trichloride) |
POCl3 |
0.064 |
0.01 |
0.12 |
0.02 |
|
| 276. |
215-242-4 |
1314-80-3 |
Phosphorus(V) sulphide,
(diphosphorus pentasulphide) |
P4S10 |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 277. |
|
7719-12-02 |
Phosphorus trichloride |
PCl3 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 278. |
231-633-2 |
7664-38-2 |
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid) |
H3PO4 |
1 |
- |
2 |
- |
- |
| 279. |
|
7723-14-0 |
Phosphorus |
P |
0.03 |
|
|
|
|
| 280. |
200-870-3 |
75-44-5 |
Phosgen (carbonyl dichloride) |
COCl2 |
0.08 |
0.02 |
0.4 |
0.1 |
- |
| 281. |
|
85-44-9
|
Phthalic anhydride
(1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, anhydride) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 282. |
|
59-87-0
|
Furacilin (nitrofural,
5-nitrofuranyl semicarbazone) |
 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 283. |
|
67-20-9
|
Furadonin
(N-(5-Nitro-2-furfurylidene)-1-aminohydantoin,
nitrofurantoin) |
 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 284. |
|
1672-88-4
|
Furagin
(N-[(5'-nitro-2'-furyl)acrylidene]-1-aminohydantoin,
N-[2-(5'-nitrofuryl-2)-2-propenylidine]-1-amino-hydantoin) |
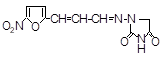 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 285. |
|
110-00-9 |
Furan |
 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 286. |
|
67-45-8
|
Furazolidone
(3-(5-nitrofurfurylidenamino)-2-oxazolidinone) |
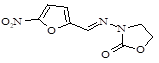 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 287. |
|
98-00-0 |
Furfuryl alcohol
(2-Hydroxymethylfuran) |
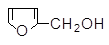 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 288. |
|
98-01-01
|
Furfural
(2-formylfuran,
2-furancarboxaldehyde) |
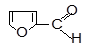 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 289. |
|
357-70-0
|
Galantamine
(herban, nururon, nivalin) |
C17H21NO3 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 290. |
|
12024-21-4 |
Gallium oxides |
Ga2O3 un
Ga2O |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 291. |
|
10038-98-9 |
Germanium (IV) chloride (after
germanium) |
GeCl4 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 292. |
|
1310-53-8 |
Germanium dioxide
(germanium (IV) oxide) |
GeO2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 293. |
|
7782-65-2
|
Germanium tetrahydride
(germane) |
GeH4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 293.1 |
200-240-8 |
55-63-0 |
Glyceryl trinitrate (nitroglycerin) |
C3H5(NO3)3 |
0.095 |
0.01 |
0.19 |
0.02 |
Skin |
| 294. |
|
111-30-8
|
Glutaraldehyd
(glutaric acid dialdehyde,
1,5-pentanedial) |
OHC(CH2)3CHO |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 295. |
|
116-16-5
|
Hexachloroacetone
(hexachloropropanone) |
Cl3CCOCCl3 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 296. |
|
118-74-1 |
Hexachlorobenzene |
C6Cl6 |
0.9 |
|
|
|
|
| 297. |
|
999-97-3 |
Hexamethyldisilazane |
(CH3)3SiNHSi(CH3)3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 298. |
|
124-09-4
|
Hexamethylenediamine
(1,6-hexanediamine,
1,6-diaminohexane) |
(NH2CH2CH2CH2)2 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 299. |
|
822-06-0
|
Hexamethylene diisocyanate
(1,6-diisocyanatohexane) |
OCN(CH2)6NCO |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 300. |
|
111-49-9
|
Hexamethyleneimine
(homopiperidine,
perhydroazepine) |
 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 301. |
203-777-6 |
110-54-3 |
n-Hexane |
C6H14 |
72 |
20 |
|
|
Auditory effect |
| 302. |
205-563-8 |
142-82-5 |
n-Heptane |
CH3(CH2)5CH3 |
350 |
85 |
2085 |
500 |
- |
| 303. |
203-767-1 |
110-43-0 |
2-Heptanone
(methyl pentyl ketone,
Methyl-amyl-ketone) |
CH3-CO-C5H11 |
238 |
50 |
475 |
100 |
Skin |
| 304. |
203-388-1 |
106-35-4 |
3-Heptanone (ethylbutylcetone) |
C2H5-CO-C4H9 |
95 |
20 |
- |
- |
- |
| 305. |
|
2499-58-3 |
Heptyl acrylate
(propenoic acid, heptyl ester,
acrylic acid, heptyl ester) |
H2C=CHCOO(CH2)6CH3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 306. |
|
111-70-6
|
Heptyl alcohol (heptanol) |
CH3(CH2)5CH2OH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 307. |
|
38066-16-9 |
Heterophos
(O-ethyl O-phenyl S-propyl phosphorothioate,
diethyl ((phenylthio)methyl)phosphonate) |
C11H17O3PS |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 308. |
206-114-9 |
302-01-2 |
Hydrazine |
NH2NH2 |
0.013 |
0.01 |
|
|
Skin |
| 308.1 |
262-967-7 |
61788-32-7 |
Hydrogen terphenyl (hydrogenated
diphenylbenzenes) |
(C6H7)3 |
19 |
2 |
48 |
5 |
|
| 309. |
|
109-78-4 |
3-Hydroxypropionitrile
(2-Cyanoethanol) |
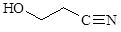 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 310. |
|
31282-04-9
|
Hygromycin B (antihelmycin) |
C20H37N3O13 |
0.001 |
|
|
|
|
| 311. |
|
91-22-5 |
Quinoline |
 |
0.1 |
|
0.5 |
|
|
| 312. |
|
627-30-5
|
3-Chloro-1-propanol
(1-chloro-3-hydroxypropane,
trimethylene chlorohydrin) |
Cl(CH2)3OH |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 313. |
|
19210-21-0 |
2-Chloro-1-propanol |
CH3CH(Cl)CH2OH |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 314. |
|
97-00-7 |
1-chloro-2,4-dinitro-benzene
(2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene) |
 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 315. |
|
127-00-4
|
1-Chloro-2-propanol
(propylene chlorohydrin) |
CH3CH(OH)CH2Cl |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 316. |
|
118-97-8 |
4-chloro-3,5-dinitro-benzoic acid |
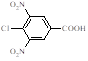 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 317. |
203-628-5 |
108-90-7 |
Chlorobenzene
(monochlorbenzene) |
C6H5Cl |
23 |
5 |
70 |
15 |
- |
| 318. |
|
106-48-9 |
4-chlorophenol |
ClC6H4OH |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 319. |
|
01/10/1120
|
9-chlorononanoic acid
(chloropelargonic acid) |
ClCH2(CH2)7COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 320. |
200-663-8 |
67-66-3 |
Chloroform (trichloromethane) |
CHCl3 |
10 |
2 |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 321. |
|
107-94-8 |
3-chloropropanoic acid |
ClCH2CH2COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 322. |
|
598-78-7
|
2-chloropropanoic acid
(α -chloropropionic acid) |
CH3CH(Cl)COOH |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 323. |
231-959-5 |
7782-50-5 |
Chlorine |
Cl2 |
1 |
0.3 |
1.5 |
0.5 |
|
| 324. |
|
57-62-5 |
Chlortetracycline |
C22H23ClN2O8 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 325. |
|
95-49-8
and
106-43-4 |
Chlorotoluene (o- and p-isomers) |
CH3C6H4Cl |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 326. |
231-595-7 |
7647-01-0 |
Hydrogen chloride |
HCl |
8 |
5 |
15 |
10 |
- |
| 327. |
|
|
Chrome, metallic (insoluble inorganic
chromium (II) chromium (III) compounds) |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 328. |
|
7789-04-0
|
Chromium (III) phosphate after
chromium
(chromium orthophosphate after chromium) |
CrPO4 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 329. |
|
1333-82-0 |
Chromium (VI) oxide
(chromium trioxide) |
CrO3 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
| 329.1 |
|
|
Chromium (VI) compounds |
|
0.005 |
|
|
|
OEV 0.010 mg/m3 until 17 January
2025.
OEV 0.025 mg/m3 for welding or plasma cutting
processes or similar work processes producing vapours until
17 January 2025 |
| 330. |
|
|
Chromium dihydrogen phosphate, after
chromium |
Cr(H2PO4)3 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 331. |
|
10060-12-5 |
Chromium trichloride hexahydrate, after
chromium |
CrCl3. 6H2O |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
| 332. |
|
1308-38-9 |
Chromium (III) oxide, after chromium |
Cr2O3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 333. |
|
7783-20-2 +
7732-18-5
|
Chromium-ammonium sulphate, after Cr
(chromium-ammonium alum) |
Cr2(SO4)3.
(NH4)2SO4.
24H2O |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 334. |
|
24613-89-6 |
Chromates,
(dichromates), after chromium |
Me2CrO4 or
Me2Cr2O7 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
| 335. |
204-662-3 |
123-92-2 |
Isoamyl acetate
(isopentyl acetate,
acetic acid 3-methylbutyl ester,
3-Methylbutyl acetate,
isopentyl ethanoate) |
CH3COOCH2CH2CH(CH3)2 |
270 |
50 |
540 |
100 |
- |
| 336. |
204-633-5 |
123-51-3 |
Isoamylalcohol,
(3-methyl-1-butanol,
isopentyl alcohol) |
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH |
18 |
5 |
37 |
10 |
|
| 336.1 |
203-745-1 |
110-19-0 |
Isobutyl acetate |
C6H12O2 |
241 |
50 |
723 |
150 |
|
| 337. |
|
121-91-5 |
Isophthalic acid
(1,3-Benzenedicarboxylic acid) |
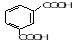 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 338. |
201-142-8 |
78-78-4 |
Iso-pentane |
H3C-CH2-CH(CH3)2 |
3000 |
1000 |
|
|
|
| 339. |
|
78-79-5 |
Isoprene
(2-methyl-1,3-butadiene) |
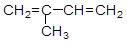 |
40 |
|
|
|
|
| 340. |
|
67-63-0
|
Isopropanol
(2-propanol, isopropyl alcohol,
1-methyl-1-ethanol) |
CH3CH(OH)CH3 |
350 |
|
600 |
|
|
| 341. |
201-245-8 |
80-05-7 |
4,4'-Isopropylidenediphenol (bisphenol
A) |
(CH3)2C(C6H4OH)2 |
25 |
- |
- |
- |
|
| 342. |
|
7553-56-2 |
Iodine |
I2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 343. |
|
2223-93-0 |
Cadmium stearate |
(CH3(CH2)16COO)2Cd |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 344. |
|
|
Cadmium and its inorganic compounds |
|
0.0015; 8 |
|
|
|
|
| 345. |
|
156-62-7 |
Calcium cyanamide |
CaNCN |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 346. |
|
7789-75-5 |
Calcium fluoride |
CaF2 |
0.5 |
|
2.5 |
|
|
| 347. |
|
7757-93-9 |
Calcium hydrogen phosphate |
CaHPO4 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 348. |
215-137-3 |
1305-62-0 |
Calcium hydroxide, (calcium
dihydroxide) |
Ca(OH))2 |
16 |
- |
46 |
|
|
| 349. |
|
7758-23-8 |
Calcium dihydrogen phosphate |
Ca(H2PO4)2 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 350. |
|
10043-52-4 |
Calcium chloride |
CaCl2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 351. |
|
471-34-1 |
Calcium carbonate |
CaCO3 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 352. |
|
|
Calcium nickel chromium phosphate (after
nickel) |
|
0.005 |
|
|
|
|
| 353. |
215-138-9 |
1305-78-8 |
Calcium oxide |
CaO |
16 |
|
46 |
|
|
| 353.1 |
|
7778-18-9 |
Calcium sulfate (hydrogenated; gypsum
dust) |
CaSO4x2H2O |
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 354. |
|
|
Potassium alkylxanthate, R=alkyl:
isopropyl-, isobutyl-, isoamyl-e
(potassium O-alkyldithiocarbonate, R-alkyl: isopropyl-,
isobutyl-, isoamyl-) |
KSCSO-R |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 355. |
|
871-58-9
|
Potassium butylxanthate
(Carbonic acid, dithio-, O-butyl ester) |
KSCSO-C4H9 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 355.1 |
205-792-3 |
151-50-8 |
Potassium cyanide (after cyanide) |
KCN |
1 |
|
5 |
|
Skin |
| 356. |
|
140-89-6
|
Ethyl potassium xanthogenate
(Potassium O-ethyl dithiocarbonate) |
KSCSO-C2H5 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 357. |
|
16871-90-2
|
Potassium fluorosilicate (after
fluorine)
(dipotassium hexafluorosilicate) |
K2[SiF6] |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 358. |
|
14459-95-1
|
Tetrapotassium hexacyanoferrate (II)
(yellow prussiate of potash) |
K4[Fe(CN)6] |
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 359. |
|
13746-66-2
|
Tripotassium hexacyanoferrate (III)
(red prussiate) |
K3[Fe(CN)6] |
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 360. |
|
3811-04-09 |
Potassium chlorate |
KClO3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 361. |
|
7447-40-7 |
Potassium chloride |
KCl |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 362. |
|
584-08-7 |
Potassium carbonate |
K2CO3 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 363. |
|
7757-79-1 |
Potassium nitrate |
KNO3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 364. |
|
7778-80-5 |
Potassium sulphate |
K2SO4 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 365. |
|
21368-68-3 |
Camphor
(DL-bornan-2-one,
1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo(2,2,1)heptan-2-one) |
C10H16O |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 366. |
203-313-2 |
105-60-2 |
e - Caprolactam (dust and vapour)
(eaminocaproic acid lactam) |
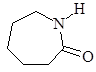 |
10 |
- |
40 |
- |
- |
| 367. |
|
142-62-1
|
Caproic acid (hexanoic acid) |
CH3(CH2)4COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 368. |
|
655-35-6
|
Carbocromen
(intencordin, Iintensain,
ethyl
-[[3-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl]oxy]acetate
hydrochloride) |
C20H27NO5 .
HCl |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 369. |
|
1302-76-7
|
Kyanite
(aluminium oxide with silicon dioxide admixture) |
Al2O5Si |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 370. |
|
50-29-3
|
Clofenotane (INN)
(1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis (4-chlorophenyl)-ethane,
dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT),
p,p'-DDT (4,4'-DDT),
1,1-bis-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trichloroethane) |
(ClC6H4)2CHCCl3 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 371. |
|
|
Cobalt hydrocarbonyl and cleavage product
thereof (after Co) |
Co(CO)4H |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
| 372. |
|
1307-96-6 |
Cobalt II oxide |
CoO |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 373. |
|
1308-04-9 |
Cobalt III oxide |
Co2O3 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 374. |
|
7440-48-4 |
Cobalt |
Co |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 375. |
|
58-08-02 |
Caffeine
(1,3, 7 - trimethylxanthine) |
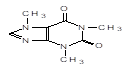 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 376. |
|
8050-09-7 |
Colophony |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 377. |
|
|
Dyes: vinyl sulphone and chloro
thiasine |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 378. |
|
|
Dyes: anthraquinone and phtalocyanine |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 379. |
|
|
Dyes, alkaline: arylmethane |
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 380. |
|
|
Dyes, vat dyes: binaphthyl hexacarboxylic
acid dianhydride derivatives |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 381. |
215-293-2 |
1319-77-3 |
Cresol, (all isomers)
(o-, m-, p-methylphenols, cresol mixture |
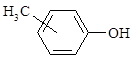 |
22 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
| 382. |
|
10453-89-1 |
Chrysanthemumic acid
(2,2-Dimethyl-3-(2-methyl-1-propenyl)
cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid) |
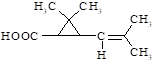 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 383. |
|
437-74-1
|
Xanthinol nicotinate
(7-[2-hydroxy-3-((2-hydroxyethyl)-N-methylamino] propyl)
theophylline nicotinate) |
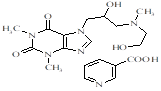 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 384. |
215-535-7 |
1330-20-7 |
Xylene
(o-, m-, p-xylene, dimethylbenzene) |
 |
221 |
50 |
442 |
100 |
Skin |
| 385. |
203-576-3 |
108-38-3 |
m-xylene,
(1,3-dimethylbenzene) |
C8H10 |
221 |
50 |
442 |
100 |
Skin |
| 386. |
202-422-2 |
95-47-6 |
o-xylene,
(1,2-dimethylbenzene) |
C8H10 |
221 |
50 |
442 |
100 |
Skin |
| 387. |
203-396-5 |
106-42-3 |
p-xylene,
(1,4-dimethylbenzene) |
C8H10 |
221 |
50 |
442 |
100 |
Skin;
Auditory effect
|
| 388. |
202-704-5 |
98-82-8 |
Cumene
(2-phenylpropane, isopropylbenzene,
propylbenzene) |
|
50 |
10 |
250 |
50 |
Skin |
| 389. |
|
25038-59-9
|
Lavsan
(polyethylene terephtalate,
terylene) |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 390. |
|
9013-95-0 |
Levan
(polysaccharide)
|
(C6H10O5)n |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 391. |
|
56-75-7 |
Levomycetin |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 392. |
|
8032-32-4
|
Ligroine (after C)
Petroleum ether) |
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
| 393. |
|
64742-82-1
|
Ligroine (naphtha, Hydrodesulfurized heavy;
naphtha treated with hydrogen with low boiling point)
(white spirit, white spirit) |
|
200 |
|
300 |
|
|
| 394. |
|
9001-62-1
|
Lipase (triacylglycerol) |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 395. |
231-
484-3 |
7580-67-8 |
Lithium hydride |
LiH |
- |
- |
0.025 |
|
|
| 396. |
|
12007-25-9 |
Magnesium diboride (after boron) |
MgB2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 397. |
|
10326-21-3 |
Magnesium chlorate |
Mg(ClO3)2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 398. |
|
12230-32-9
|
Magnesium polyboride
(Magnesium dodecaboride)
|
MgB12 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 399. |
|
|
Magnesium- manganese ferrite |
MgMn(FeO2)4 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 400. |
|
108-31-6
|
Maleic anhydride
(maleinanhydride,
1,2-ethylendicarbonic acid anhydride) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 401. |
|
1313-13-9 |
Manganese dioxide (disintegration
aerosol) |
MnO2 |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 401.1 |
|
|
Manganese and its inorganic compounds (after
manganese) |
|
0.25
0.056
|
|
|
|
|
| 402. |
|
07/05/3353 |
Manganese distearate |
[CH3(CH2)16COO]2Mn |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 403. |
|
12108-13-3
|
Manganese cyclopentadienyl tricarbonyl
(Tricarbonyl(methylcyclopentadienyl)manganese)
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 404. |
|
12427-38-2
|
Manganese,
ethylene-N,N-bis-dithiocarbamate
(maneb) |
 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 405. |
|
|
Manganese-zinc ferrite |
MnZn(FeO2)4 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 406. |
|
7439-96-5 |
Manganese welding aerosol (condensation
aerosol) |
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 407. |
|
8065-48-3
|
Mercaptophos
(demeton,
O,O-diethyl-O''-(2-ethylthioethyl) thiophosphate and
O,O'-diethyl-S-(2-ethylthioethyl) thiophosphate mixture) |
C2H5SCH2CH2OPS(OC2H5)2
un
C2H5SCH2CH2SPO(OC2H5)2 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 408. |
|
79-39-0
|
Methylacrylic amide
(2-methylpropionic acid amide) |
CH2=C(CH3)CONH2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 409. |
|
79-41-4
|
Methacrylic acid
(2-2-methylpropionic acid) |
CH2=C(CH3)COOH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 410. |
|
760-93-0
|
Methacrylic acid anhydride
(2-methylpropenoic acid anhydride,
methacrylic anhydride) |
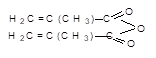 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 411. |
|
920-46-7
|
Methacrylic acid chloroanhydride
(methacrylic chloride,
2-methylpropenoic acid chloroanhydride) |
CH2=C(CH3)COCl |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 412. |
|
74-93-1
|
Methanethiol (methyl mercaptan) |
CH3SH |
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
| 413. |
200-659-6 |
67-56-1 |
Methanol
(methyl alcohol, carbinol) |
CH3OH |
260 |
200 |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 414. |
|
1569-50-2
|
3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol
(3-Penten-3-ol,
2,2-dimethylvinylcarbinols) |
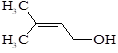 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 415. |
|
80-59-1
|
2-methylbut-2-enoic acid
2-methylcrotonic acid,
2,3-dimethylacrylic acid) |
CH3CH=C(CH3)COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 416. |
|
638-10-8
|
3-methylbut-2-enoic acid ethyl ester
(3,3-dimethylacrylic acid ethyl ester,
crotonic acid, 3-methyl-, ethyl ester) |
(CH3)2C=CHCOOCH2CH3 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 417. |
|
3425-61-4
|
2-hydroperoxy-2-methyl-butane
(tert-Pentyl hydroperoxide) |
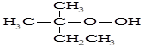 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 418. |
|
79-20-9
|
Methyl acetate
(acetic acid, methyl ester) |
CH3COOCH3 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
| 419. |
|
96-33-3
|
Methyl acrylate (methyl propenoate, acrylic
acid, methyl ester, propenoic acid, methyl ester) |
CH2=CHCOOCH3 |
18 |
5 |
36 |
10 |
|
| 420. |
|
74-83-9
|
Methyl bromide (bromomethane) |
CH3Br |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 421. |
210-946-8 |
626-38-0 |
1-Methylbutyl acetate,
(1-methylbutyl ethanoate) |
CH3COOCH(CH3)CH2CH2CH3 |
270 |
50 |
540 |
100 |
- |
| 421.1 |
203-481-7 |
107-31-3 |
Methyl formate (formic acid methyl
ester) |
HCOOCH3 |
125 |
50 |
250 |
100 |
Skin |
| 422. |
203-737-8 |
110-12-3 |
5-Methyl-2-hexanone
(isopentyl methyl ketone,
isoamyl methyl ketone,
isobutyl acetone) |
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2COCH3 |
95 |
20 |
- |
- |
- |
| 423. |
208-793-7 |
541-85-5 |
5-Methyl-3-heptanone
(ethylisoamylketone) |
CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2COCH2CH3 |
53 |
10 |
107 |
20 |
- |
| 424. |
203-550-1 |
108-10-1 |
4-Methyl-2-pentanone,
(isobutyl methyl ketone,
methylisobutylketone,
isopropyl acetate) |
CH3C(O)CH2CH(CH3)CH3 |
83 |
20 |
208 |
50 |
- |
| 425. |
|
872-50-4
|
1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone
(N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone) |
C5H9NO |
40 |
10 |
80 |
20 |
Skin |
| 426. |
208-601-1 |
534-52-1 |
2-methyl-4,6-dinitro-phenol
(4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol, DNOC) |
(CH3)
C6H2(NO2)2OH |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 427. |
|
74-95-3
|
Methylene bromide
(dibromomethane) |
CH2Br2 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 427.1 |
202-974-4 |
101-77-9 |
4,4'-methylenedianiline
(4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane) |
C13H14N2 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
Skin |
| 427.2 |
202-918-9 |
101-14-4 |
4,4'-methylene bis (2-chloroaniline) |
C13H12Cl2N2 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
Skin |
| 428. |
200-838-9 |
75-09-2 |
Methylene chloride (dichloromethane) |
CH2Cl2 |
120 |
34 |
150 |
42 |
Skin |
| 429. |
200-817-4 |
74-87-3
|
Methyl chloride (chloromethane) |
CH3Cl |
42 |
20 |
|
|
|
| 429.1 |
205-599-4 |
143-33-9 |
Sodium cyanide (after cyanide) |
NaCN |
1 |
|
5 |
|
Skin |
| 430. |
|
624-83-9 |
Methylisocyanate |
CH3N=C=O |
|
|
0.05 |
0.02 |
|
| 431. |
|
563-80-4
|
Methyl isopropyl ketone
(3-Methyl-2-butanone) |
CH3C(O)C(CH3)CH3 |
200 |
|
|
|
|
| 432. |
|
556-61-6 |
Methyl isothiocyanate |
CH3N=C=S |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 433. |
|
8022-00-2
|
Methyl mercaptophos (demeton-methyl,
O,O'-dimethyl-O''-(2-ethylthioethyl) thiophosphate and
dimethyl-S-(2-ethylthioethyl) thiophosphate mixture) |
S=P(OCH3)2-O-(CH2)2S-C2H5
un
S=P(OCH3)2-S-(CH2)2S-C2H5 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 434. |
|
80-62-6
|
Methyl methacrylate
2-methyl-2-propenoic acid methyl ester,
methyl 2-methylpropenoate) |
CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 435. |
|
25013-15-4
|
Methylstyrene (mixed isomers)
(vinyltoluene, vinylbenzene) |
CH2=CH-C6H4CH3 |
50 |
|
|
|
Auditory effect |
| 436. |
|
98-83-9
|
α-Methylstyrene
(2-phenylpropene) |
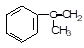 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 437. |
|
598-50-5
|
Methylurea (N-Methylurea) |
CH3NHC(O)NH2 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 438. |
|
78-94-4 |
Methyl-vinyl-ketone
(3-butene-2-one) |
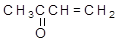 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 439. |
|
|
Welding aerosol |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 439.1 |
|
110-49-6 |
2-Methyoxyethyl acetate |
C5H10O3 |
|
1 |
|
|
Skin |
| 439.2 |
|
109-86-4 |
2-Methoxyethanol |
C3H8O2 |
|
1 |
|
|
Skin |
| 440. |
203-603-9 |
108-65-6 |
2-methoxy-1-methylethyl acetate (propylene
glycol monomethyl ether acetate) |
CH3COOCH(CH3)CH2OCH3 |
275 |
50 |
550 |
100 |
Skin |
| 441. |
252-104-2 |
34590-94-8 |
Methoxyisopropoxy propanol
(dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether, DMP) |
CH3OC3H6OC3H6OH |
308 |
50 |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 442. |
203-539-1 |
107-98-2 |
1-Methoxy-2-propanol
(propylene glycol monomethyl ether, monopropylene glycol
methyl ether) |
CH3CH(OH)CH2OCH3 |
375 |
100 |
568 |
150 |
Skin |
| 443. |
|
586-37-8 |
m-Methoxyacetophenone
(3-acetylanisole,
3-acetylmethoxybenzene) |
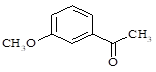 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 444. |
203-906-6 |
111-77-3 |
2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethanol |
C5H12O3 |
50.1 |
10 |
|
|
Skin |
| 445. |
203-604-4 |
108-67-8 |
Mesitylene
(1,3,5-trimethylbenzene) |
|
100 |
20 |
- |
- |
- |
| 446. |
|
79-11-08
|
Monochloroacetic acid
(chloroacetic acid) |
ClCH2COOH |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 447. |
|
79-04-09
|
Monochloroacetic acid chloroanhydride
(chloroacetyl chloride) |
CH2ClCOCl |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 448. |
203-815-1 |
110-91-8 |
Morpholine |
C4H9NO |
36 |
10 |
72 |
20 |
|
| 449. |
202-049-5 |
91-20-3 |
Naphthalene |
 |
50 |
10 |
- |
- |
- |
| 450. |
|
8030-30-6 |
Petroleum |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 451. |
|
|
Mineral oils, petroleum mineral oils |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 452. |
|
1141-38-4 |
2,6-Naphthalenedicarboxylic acid |
 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 453. |
|
93-09-4
|
2-Naphthalenecarboxylic acid
(2-naphthoic acid) |
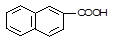 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 454. |
|
128-97-2 |
1,4,5,8-Naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid |
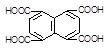 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 455. |
|
130-15-4 |
1,4-Naphthoquinone |
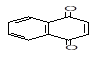 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 456. |
|
90-15-3
|
1-Naphthol
(1-hydroxynaphthalene,
α-naphthol) |
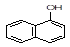 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 457. |
|
135-19-3
|
2-Naphthol
(2-hydroxynaphthalene,
β-naphthol) |
 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 458. |
247-852-1 |
26628-22-8 |
Sodium azide |
NaN3 |
0.1 |
- |
0.3 |
- |
Skin |
| 459. |
|
4312-97-4
|
Sodium cis- β -chloroacrylate
(acrofol,
cis-3-Chloroacrylic acid sodium salt,
cis-3-chloropropenoic acid sodium salt, sodium
3-chloroacrylate) |
 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 460. |
|
16893-85-9 |
Sodium hexafluorosilicate |
Na[SiF6] |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 461. |
|
144-55-8
|
Sodium hydrogencarbonate
(baking soda) |
NaHCO3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| 462. |
|
1310-73-2
|
Sodium hydroxide
(soda lye, caustic soda) |
NaOH |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 463. |
|
7775-09-09 |
Sodium chlorate |
NaClO3 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 464. |
|
7647-14-5 |
Sodium chloride |
NaCl |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 465. |
|
7758-19-2 |
Sodium chlorite |
NaClO2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 466. |
|
137-42-8
|
Sodium N-methyldithiocarbamate
(methyldithiocarbamate,
methyldithiocarbamic acid, sodium salt,
carbathione) |
CH3-NH-C(S)SNa |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 467. |
|
131-52-2 |
Sodium pentachlorophenolate |
C6Cl5ONa |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 468. |
|
10332-33-9 |
Sodium perborate monohydrate |
NaBO3 . H2O |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 469. |
|
10486-00-7 |
Sodium perborate tetrahydrate |
NaBO3 . 4H2O |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 470. |
|
540-72-7
|
Sodium rhodanide
(sodium thiocyanate) |
NaSCN |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 471. |
|
7757-82-6 |
Sodium sulphate |
Na2SO4 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 472. |
|
1313-82-2 |
Sodium sulphide |
Na2S |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 473. |
207-343-7 |
463-82-1 |
Neopentane |
C5H12 |
3000 |
1000 |
|
|
|
| 474. |
200-193-3 |
54-11-5 |
Nicotine,
(3-(1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl) pyridine) |
 |
0.5 |
- |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 475. |
|
59-67-6
|
Nicotinic acid
(pyridine-3-carboxylic acid) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 476. |
|
98-92-0
|
Nicotine acid amide
(pyridine-3-carboxylic acid amide, nicotinamide) |
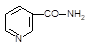 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 477. |
|
7440-02-0 |
Nickel, nickel oxides, sulphides and
compounds (after Ni) |
Ni |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 478. |
|
13977-71-4 |
Nickel chromophosphate |
NiCr(H2PO4)6 .
H2O |
0.005 |
|
|
|
|
| 479. |
|
13463-39-3
|
Nickel carbonyl
(tetracarbonyl nickel) |
Ni(CO)4 |
0.0005 |
|
|
|
|
| 480. |
|
53025-58-4 |
Nitro |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 481. |
|
88-74-4 |
2-nitroaniline (o-nitroaniline) |
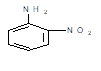 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 482. |
|
99-09-2 |
3-nitroaniline (m-nitroaniline) |
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 483. |
|
100-01-6
|
4-nitroaniline
(p-nitroaniline) |
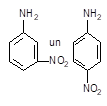 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 484. |
|
100-17-4 |
4-nitroanisole
(1-Methoxy-4-nitrobenzene) |
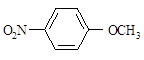 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 485. |
202-716-0 |
98-95-3 |
Nitrobenzene |
|
1 |
0.2 |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 486. |
|
585-79-5 |
m-Nitrobromobenzene
(1-Bromo-3-nitrobenzene) |
 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 487. |
201-188-9 |
79-24-3 |
Nitroethane |
CH3CH2NO2 |
30 |
9.6 |
312 |
100 |
Skin |
| 488. |
|
75-52-5 |
Nitromethane |
CH3NO2 |
30 |
|
|
|
|
| 488.1 |
201-209-1 |
79-46-9 |
2-nitropropane |
 |
18 |
5 |
|
|
|
| 489. |
|
88-72-2
99-08-1
99-99-0 |
Nitrotoluene
(o-, m-, p-isomers) |
 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 490. |
|
502-56-7 |
Nonan-5-one |
CH3(CH2)7CO(CH2)3CH3 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
| 491. |
|
143-08-8 |
Nonyl alcohol (nonanol) |
CH3(CH2)7CH2OH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 492. |
204-696-9 |
124-38-9 |
Carbon dioxide |
CO2 |
9000 |
5000 |
- |
- |
- |
| 493. |
211-128-3 |
630-08-0 |
Carbon (II) oxide (carbon monoxide, carbon
monoxide gas) |
CO |
20 |
17 |
117 |
100 |
Auditory effect |
| 494. |
|
|
Carbon dust |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- coal,
anthracite and other coal dust, petroleum, coke, bituminous
shale, black industrial soot |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
- natural and artificial diamonds,
graphite |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 495. |
|
|
Hydrocarbons, saturated aliphatic, C1-10
after C
(alkanes) |
CnH2n+2 |
100 |
|
300 |
|
|
| 496. |
|
66-79-5 |
Oxacillin |
C19H19N3O5S |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 497. |
|
111-87-5 |
Octyl-alcohol
(octanol) |
CH3(CH2)6CH2OH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 498. |
|
7060-74-4 |
Oleandomycin phosphate |
C35H61NO12.H3PO4 |
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
| 499. |
|
10028-15-6 |
Ozone |
O3 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 500. |
|
422-64-0 |
Propanoic acid, pentafluoro- |
CF3CF2COOH |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 501. |
203-692-4 |
109-66-0 |
Pentane |
C5H12 |
3000 |
1000 |
|
|
|
| 502. |
|
8006-61-9 |
Kerosene |
|
100 |
|
300 |
|
|
| 503. |
201-865-9 |
88-89-1 |
Picric acid,
(2,4,6-trinitrophenol) |
 |
0.1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 504. |
203-808-3 |
110-85-0 |
Piperazine
(diethylenediamine) |
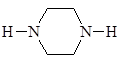 |
0.1 |
- |
0.3 |
- |
- |
| 505. |
|
110-89-4 |
Piperidine |
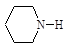 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
|
| 506. |
232-319-8 |
8003-34-7 |
Pyrethrins and pyrethroids
(pyrethrum (purified from sensitising lactones)) |
Multicomponent insecticide of plant
origin |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 507. |
203-809-9 |
110-86-1 |
Pyridine |
|
15 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
| 508. |
|
123-75-1 |
Pyrrolidine |
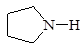 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 509. |
231-116-1 |
04/06/7440 |
Platinum (metal) |
Pt |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 510. |
|
|
Polymer dust: (polyamide, polyformaldehyde,
polycaprolactam, polyethylene, polymers in the basis of which
there are acrylic monomers, polypropene, polyurethane
etc.) |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 511. |
|
107-19-7 |
Propargyl alcohol
(2-Propyn-1-ol) |
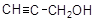 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 511.1 |
|
74-98-6 |
Propene |
CH3CH2CH3 |
1800 |
1000 |
|
|
|
| 512. |
201-176-3 |
79-09-4 |
Propanoic acid
(propionic acid) |
C2H5COOH |
31 |
10 |
62 |
20 |
- |
| 513. |
|
109-60-4 |
Propyl acetate
(acetic acid, propyl ester) |
CH3COOC3H7 |
200 |
|
|
|
|
| 514. |
|
107-10-8 |
Propylamine
(n-propylamine) |
NH2C3H7 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 515. |
|
108-32-7
|
Propylene carbonate
(1,2-Propanediol cyclic carbonate) |
 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 516. |
|
|
Propylene glycol monoacrylate |
CH2=CHCOO-CH2-CH2OH-CH3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 517. |
|
57-55-6
|
propylene glycol
(1,2-propanediol) |
CH3CH(OH)CH2OH |
7 |
|
|
|
|
| 518. |
200-879-2 |
75-56-9
|
Propylene oxide (methyloxirane,
1,2-epoxypropane) |
 |
2.4 |
1 |
|
|
|
| 519. |
|
115-07-1
|
Propylene (propene) |
CH2=CH-CH3 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
| 520. |
|
106-36-5
|
Propyl propionate
(propionic acid propyl ester) |
CH3CH2COOC3H7 |
70 |
|
|
|
|
| 521. |
|
71-23-8
|
Propyl alcohol (1-propanol) |
CH3CH2CH2OH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 522. |
|
123-38-6
|
Propionaldehyde (propanal) |
CH3CH2CHO |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 523. |
|
|
Dust of plant and animal origin: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
sugar dust |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
grain dust |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cotton, linen, wool, piles etc. (with an
admixture of silicon dioxide):
* more than 10 %
*less than 10 % |
|
2 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
flour dust |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
wood dust |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
peat dust |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
hardwood dust7 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
OEV 3mg/m3 until 17 January
2023 |
|
|
|
paper dust |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8037-19-2 |
tobacco dust |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
| |
tea dust |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 524. |
|
|
Yeast (dry) |
|
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 525. |
203-585-2 |
108-46-3 |
Resorcinol
(1, 3-dihydroxybenzene benzene-1,3-diol) |
 |
45 |
10 |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 526. |
|
83-88-5 |
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) |
C17H20N4O6 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 527. |
|
13292-46-1 |
Rifampicin (rimactane) |
|
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 528. |
|
111-20-6 |
Sebacic acid
(1,8- octane dicarboxylic acid) |
HOOC(CH2)8COOH |
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 528.1 |
203-300-1 |
105-46-4 |
Sec-butyl acetate |
C6H12O2 |
241 |
50 |
723 |
150 |
|
| 529. |
231-978-9 |
7783-07-5 |
Hydrogen selenide |
H2Se |
0.07 |
0.02 |
0.17 |
0.05 |
- |
| 530. |
231-195-2 |
7446-09-5 |
Sulphur (IV) oxide (sulphur dioxide) |
SO2 |
1.3 |
0.5 |
2.7 |
1 |
|
| 531. |
|
7446-11-9
|
Sulphur (VI) oxide
(sulphuric anhydride, sulphur trioxide) |
SO3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 532. |
|
10025-67-9 |
Sulphur monochloride
(disulphur dichloride) |
S2Cl2 |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 533. |
|
75-15-0 |
Carbon disulphide |
CS2 |
15 |
5 |
|
|
Skin;
Auditory effect |
| 534. |
|
7704-34-9 |
Sulphur |
S |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 535. |
|
7664-93-9 |
Sulphuric acid3 (mist defined as
the thoracic fraction) |
H2SO4 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 536. |
|
7783-06-4 |
Hydrogen sulphide |
H2S |
7 |
5 |
14 |
10 |
|
| 537. |
|
|
Hydrogen sulphide mixed with hydrocarbons
C1-C5 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 538. |
|
7631-86-9 |
Silicon dioxide |
SiO2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 538.1 |
|
|
Inhalable crystalline silica dust |
|
0.15 |
|
|
|
|
| 539. |
|
409-21-2 |
Silicon carbide |
SiC |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 540. |
|
12033-89-5 |
Silicon nitride
(trisilicon tetranitride) |
Si3N4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 541. |
|
12007-81-7 |
Silicon tetracboride
(tetraboron silicide) |
SiB4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 542. |
|
|
Silicon and copper alloy |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 543. |
|
|
Silicates and aluminosilicates: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
abrasive dust |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bauxite agglomerate |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mica,
phlogopite, muscovite, talc, talc type dust |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
artificial mineral fibres with silicate and
aluminosilicate glassy structure (glass-fiber, glass-wool,
slag and mineral wool etc.) |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mineral fibres, including rock wool, glass
fibre |
|
3 sol/cm3 air |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cement, apatite, clay |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
glassy silicates of volcanic origin (tuff,
pemza, perlite) |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
zeolites (artificial and natural) |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pottery |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ceramic fibres (fireproof) |
|
0.3 sol/cm3
air |
|
|
|
|
| |
16389-88-1 |
dolomite |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 544. |
|
77348-01-7 |
Sylvinite |
Cl2KNa |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 545. |
|
|
Synthetic detergents |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 546. |
205-634-3 |
144-62-7 |
Oxalic acid
(ethanedioic acid) |
HOOCCOOH |
1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 547. |
|
|
Mixture of dialkyl diesters of oxalic
acid
(dialkyloxalates) |
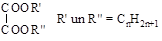 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 548. |
200-579-1 |
64-18-6 |
Formic acid (methanoic acid) |
HCOOH |
9 |
5 |
- |
- |
- |
| 549. |
233-272-6 |
10102-44-0 |
Nitrogen dioxide |
NO2 |
0.96 |
0.5 |
1.91 |
1 |
|
| 550. |
233-271-0 |
10102-43-9 |
Nitrogen monoxide |
NO |
2.5 |
2 |
- |
- |
|
| 551. |
|
|
Nitrogen oxides, (after NO2) |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 552. |
231-714-2 |
7697-37-2 |
Nitric acid |
HNO3 |
2 |
0.78 |
2.6 |
1 |
|
| 553. |
|
|
Fiber glass in the basis of which there is
polyester resin |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 554. |
|
100-42-5
|
Styrene (vinylbenzene) |
C6H5CH=CH2 |
10 |
|
30 |
|
Auditory effect |
| 555. |
|
57-92-1
|
Streptomycin
(agrimycin, phytomycin) |
C21H39N7O12 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 556. |
231-131-3 |
7440-22-4 |
Silver metal |
Ag |
0.1 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| 557. |
|
|
Silver soluble compounds |
After Ag |
0.01 |
- |
|
|
|
| 558. |
|
57-68-1
|
Sulfadimidine
(sulphamethazine, sulfodimesin,
4-amino-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 559. |
|
57-67-0
|
Sulfaguanidine
(sulfanilylguanidine, sulgin,
4-amino-N-(aminoiminomethyl)-benzenesulfonamide) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 560. |
|
547-44-4 |
Sulfacarbamide |
H2N-C6H4-SO2NHC(O)NH2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 561. |
|
152-47-6 |
Sulfalene
(4-Amino-N-(3-methoxypyrazin- 2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide) |
 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 562. |
|
651-06-9 |
Sulfametoxydiazine
(5-methoxysulfadiazine,
4-amino-N-(5-methoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)-benzenesulfonamide) |
 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 563. |
|
80-35-3 |
Sulphamethoxypyridazine
(sulphanilic acid 6-methoxy-3-pyridazinyl amide,
4-amino-N-(6-methoxy-pyridazin-3-yl)-benzenesulfonamide) |
 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 564. |
|
63-74-1
|
Sulfanilamide
(streptocide,
4-aminobenzenesulfonamide) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 565. |
|
72-14-0 |
Sulfathiazol
(4-amino-N-(thiazol-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide,
sulphanilic acid thiazol-2-ylamide,
norsulfazole) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 566. |
222-995-2 |
3689-24-5 |
Sulfotep
(tetraethyldithiopyrophosphate,
1,2-dithiodiphosphoric acid, tetraethyl ester) |
C8H20O5P2S2 |
0.1 |
- |
- |
- |
Skin |
| 567. |
|
107-92-6 |
Butyric acid (butanoic acid) |
CH3(CH2)2COOH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 568. |
|
123-72-8 |
Butyraldehyde
(butyraldehyde, butanal) |
CH3(CH2)2CHO |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 569. |
|
57218-73-2 |
Lead hydrocyanate |
|
0.005 |
|
|
|
|
| 570. |
|
15748-73-9 |
Lead disalicylate
(2-hydroxybenzoato-lead salt) |
(HOC6H4COO)2Pb |
0.005 |
|
|
|
|
| 571. |
|
7439-92-1 |
Lead and its inorganic compounds, (after
lead) |
Pb |
0.05 |
|
0.1 |
|
Auditory effect |
| 572. |
|
|
Chamotte-graphite fireproof material |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 573. |
|
1401-55-4 |
Tannin |
C76H52O46 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 574. |
|
13494-80-9 |
Tellurium |
Te |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
| 575. |
|
83-67-0 |
Theobromine
(3,7-dimethylxanthine,
3,7-dihydro-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione) |
 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 576. |
|
58-55-9 |
Theophylline
(1,3-dimethylxanthine,
3,7-dihydro-1,3-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione) |
 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 577. |
208-760-7 |
540-88-5 |
Tert-butyl acetate |
C6H12O2 |
200 |
|
|
|
|
| 577.1 |
|
1634-04-4 |
Methyl tert-butyl ether |
C5H12O |
183.5 |
50 |
367 |
100 |
|
| 578. |
|
9005-90-7 |
Essence of turpentine |
C10H16 |
300 |
|
|
|
|
| 579. |
|
60-54-8 |
Tetracycline |
C22H24N2O8 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 579.1 |
201-083-8 |
78-10-4 |
Tetraethyl orthosilicate (ethyl silicate;
tetraethoxysilane) |
(C2H5O)4Si |
44 |
5 |
|
|
|
| 580. |
|
78-00-2 |
Tetraethyl lead |
(C2H5)4Pb |
0.005 |
|
|
|
|
| 581. |
|
127-21-9 |
1,1,3,3-Tetrafluoro-1,3-dichloropropan-2-on
(tetrafluoro-1,3-dichloroacetone)
|
ClF2CCOCF2Cl |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 582. |
|
76-37-9 |
2,2,3,3-Tetrafluoropropan-1-ol |
CHF2-CF2-CH2OH |
20 |
|
|
|
|
| 583. |
203-726-8 |
109-99-9 |
Tetrahydrofuran |
 |
150 |
50 |
300 |
100 |
Skin |
| 584. |
|
79-34-5 |
1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane |
CHCl2CHCl2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 585. |
|
25322-20-7 |
Tetrachloroethane (mixed isomers) |
C2H2Cl4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 586. |
204-825-9 |
127-18-4 |
Tetrachloroethylene (perfluoroethylene) |
C2Cl4 |
70 |
10 |
140 |
20 |
Skin |
| 587. |
200-262-8 |
56-23-5 |
Carbon tetrachloride (carbon tetracloride,
tetrachlormethane) |
CCl4 |
6.4 |
1 |
32 |
5 |
Skin |
| 588. |
|
1401-69-0 |
Tylosin |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 589. |
|
68-11-01 |
Thioglycolic acid |
HSCH2COOH |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 590. |
|
62-56-6 |
Thiourea |
NH2CSNH2 |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| 591. |
|
12039-13-3 |
Titanium disulphide |
TiS2 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 592. |
|
25583-20-4 |
Titanium nitride |
TiN |
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 593. |
|
12039-83-7 |
Titanium disilicide |
TiSi2 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 594. |
|
7440-32-6 |
Titanium |
Ti |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 595. |
|
13463-67-7 |
Titanium dioxide |
TiO2 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 596. |
202-429-0 |
95-53-4 |
o-toluidine |
CH3C6H4NH2 |
0.5 |
0.1 |
|
|
Skin |
| 597. |
|
108-44-1 |
m-toluidine |
CH3C6H4NH2 |
0.5 |
|
1 |
|
|
| 598. |
203-403-1 |
106-49-0 |
P-toluidine (4-aminotoluene) |
CH3C6H4NH2 |
4.46 |
1 |
8.92 |
2 |
Skin |
| 599. |
|
584-84-9 |
2,4-toluene diisocyanate
(methyl-m-phenylene diisocyanate,
toluene-2,4-diisocyanate,
m-tolylidene diisocyanate) |
C9H6N2O2 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
|
| 600. |
203-625-9 |
108-88-3 |
Toluene (methylbenzol) |
CH3C6H5 |
50 |
14 |
150 |
40 |
Skin;
Auditory effect |
| 601. |
|
49721-45-1
|
4,5,6-Triaminopyrimidine sulphate
(pyrimidine-4,5,6-triamino sulphate) |
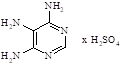 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 602. |
|
559-11-5 |
2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,7-Tridecafluoroheptyl acrylate
(acrylic acid 1H, 1H- tridecafluoroheptyl ester,
2-propenoic acid
2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,7-tridecafluoroheptyl ester) |
H2C=CHCOOCH2(CF2)5CF3 |
30 |
|
|
|
|
| 603. |
204-469-4 |
121-44-8 |
Triethylamine |
(C2H5)3N |
8.4 |
2 |
12.6 |
3 |
- |
| 603.1 |
200-875-0 |
75-50-3 |
Trimethylamine |
C3H9N |
4.9 |
2 |
12.5 |
5 |
|
| 604. |
204-428-0 |
120-82-1 |
1,2,4-trichlorobenzene |
 |
15, 1 |
2 |
37, 8 |
5 |
Skin |
| 605. |
200-756-3 |
71-55-6 |
1,1,1-trichloroethane (methyl
chloroform) |
CH3CCl3 |
555 |
100 |
1110 |
200 |
|
| 606. |
|
461-18-7 |
4,4,4-Trifluoro-1-butanol |
CF3(CH2)3OH |
20 |
|
|
|
|
| 607. |
|
507-52-8 |
1,1,1-trifluoro-2-methyl-propan-2-ol |
(CH3)2C(OH)CF3 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
| 608. |
|
75-89-8 |
2,2,2-trifluoroethanol |
CF3CH2OH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 609. |
|
420-46-2
|
1,1,1-trifluoroethane (Freon 143) |
CH3CF3 |
3000 |
|
|
|
|
| 610. |
|
76-05-1 |
1,1,1-trifluoroacetic acid |
CF3COOH |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 611. |
|
25854-04-0 |
1,1,2-trichloro-1,3-butadiene |
Cl2C=CCl-CH=CH2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 612. |
|
75-87-6
|
Trichloroacetaldehyde (chloral) |
CCl3CHO |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 613. |
|
76-03-9 |
Trichloroacetic acid |
CCl3COOH |
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 614. |
|
76-02-8 |
Trichloroacetic acid chloroanhydride |
CCl3COCl |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 615. |
201-167-4 |
79-01-6 |
Trichloroethylene (trichloroethene) |
ClCH=CCl2 |
54.7 |
10 |
164.1 |
20 |
Skin |
| 616. |
|
5329-12-4 |
2,4,6-trichlorophenylhydrazine |
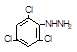 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 617. |
|
96-18-4 |
1,2,3-trichloropropane |
ClH2C-CHCl-CH2Cl |
2 |
|
|
|
|
| 618. |
|
3278-46-4 |
2,2,3-trichloropropanoic acid
(chloropon) |
ClCH2CCl2COOH |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 619. |
|
96-19-5 |
1,2, 3-Trichloropropene |
ClHC=CCl-CH2Cl |
3 |
|
|
|
|
| 620. |
|
10025-78-2 |
Trichlorsilan, after HCl |
SiHCl3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 621. |
|
2077-46-5 |
2,3,6- trichlorotoluene |
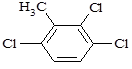 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 622. |
208-394-8 |
526-73-8 |
1,2,3-trimethylbenzene |
 |
100 |
20 |
- |
- |
- |
| 623. |
202-436-9 |
95-63-6 |
1,2,4-trimethylbenzene
(pseudocumol) |
 |
100 |
20 |
- |
- |
- |
| 624. |
|
118-96-7 |
2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) |
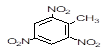 |
0.1 |
|
0.5 |
|
|
| 625. |
|
7440-61-1 |
Uranium, insoluble compounds |
U |
0.075 |
|
|
|
|
| 626. |
|
7440-61-1 |
Uranium, soluble compounds |
U |
0.015 |
|
|
|
|
| 627. |
|
57-13-6 |
Urea |
NH2CONH2 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 628. |
|
|
Urosulfane (sulfanilcarbamide) |
H2N-C6H4-SO2NHC(O)NH2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 629. |
|
1314-34-7 |
Vanadium trioxide dust (disintegration
aerosol)
(divanadium trioxide dust (disintegration aerosol) |
V2O3 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 630. |
|
1314-62-1 |
Vanadium pentaoxide smoke (condensation
aerosol)
(divanadium pentaoxide smoke (condensation aerosol) |
V2O5 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 631. |
|
7440-62-2
|
Vanadium and its compounds
(ferro-vanadium (after vanadium)) |
V |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 632. |
|
|
Slag dust containing vanadium |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 633. |
|
12019-57-7 |
Copper phosphide
(tricopper phosphide) |
Cu3P |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 634. |
|
147-14-8 |
Copper-phthalocyanine |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
| 635. |
|
17836-27-0 |
Copper chromium phosphate, after
CrO3 |
|
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
| 636. |
|
20936-31-6 |
Copper salicylate
(salycilic acid copper salt) |
Cu(C7H5O3)2 .
4H2O |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 637. |
|
7758-89-6 |
Copper salt after copper (chloric acid, ch.
acid, sulphuric acid etc.) |
(Cu) |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 638. |
|
25267-55-4 |
Copper trichlorophenolate |
Cu(C6H2OCl3)2 |
0.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 639. |
|
7440-50-8 |
Copper |
Cu |
0.5 |
|
1 |
|
|
| 640. |
|
88-12-0 |
1`-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone
(N-Vinylpyrrolidone) |
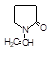 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
| 641. |
|
108-05-4 |
Vinyl acetate (acetic acid, vinyl
ester) |
CH3COOCH=CH2 |
17.6 |
5 |
35.2 |
10 |
|
| 642. |
|
689-97-4 |
Vinyl acetylene (1-butene-3-yne) |
HCCCHCH2 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
| 643. |
|
|
vinyl-phosphonicacid dichloro ethyl
ester |
CH2=CHP(O)(OCH2CH2Cl)2 |
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
| 644. |
200-831-0 |
75-01-4 |
Vinyl chloride monomer (chloroethylene) |
CH2=CHCl |
2.6 |
1 |
|
|
|
| 645. |
|
|
Polymers of vinyl chloride and vinylidene
chloride |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
| 645.1 |
200-864-0 |
75-35-4 |
Vinylidene chloride
(1,1-dichloroethylene) |
C2H2Cl2 |
8 |
2 |
20 |
5 |
|
| 646. |
|
100-69-6 |
2-vinylpyridine |
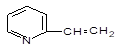 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 647. |
|
12070-12-1 |
Tungsten carbide |
WC |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 648. |
|
12039-88-2 |
Tungsten disilicide |
WSi2 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
| 649. |
|
|
Tungsten-cobalt alloy with diamond admixture
up to 5 % |
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
| 650. |
|
|
Vulcanisation gases which arise in tyre
manufacturing and in the production of other rubber
articles |
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
| 651. |
|
81-81-2 |
Zoocoumarin (warfarin,
3-(α-acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin,
(R)-4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-butyl)-2-benzopyrone,
(S)-4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-butyl)-2-benzopyrone) |
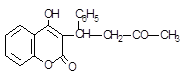 |
0.001
|
|
|
|
|
Notes:
1 - EINECS - the substance number in the European Inventory of
Existing Chemical substances;
2 - CAS - Chemical Abstract Service Number - the
registration number of the substance in the reference publication
Chemical Abstract;
3 -When selecting an appropriate exposure monitoring method,
account should be taken of potential limitations and
interferences that may arise in the presence of other sulphur
compounds.
4 - Short-term exposure limit regarding the base time period
of one minute.
5 - Inhalable fraction.
6 - Fraction which may enter into the respiratory tract.
7 - Inhalable fraction: If hardwood dust is mixed with other
wood dust, the limit value shall apply to all types of dust
present in that mixture.
8 - Inhalable fraction if biomonitoring approach is not
implemented. Respirable fraction for cadmium by using
biomonitoring approach with a biological exposure indicator not
exceeding 2 µg Cd/g of creatinine in urine shall be in force
until 11 July 2027.
Acting for the Minister for
Welfare,
Minister for the Environment R. Vējonis
In Revised
Version Submitted by the Ministry of Welfare
Annex 2
Cabinet
Regulation No. 325
15 May 2007
Synonyms of Chemical Substances
and Numbers Corresponding to Substances
[1 February 2011; 7 April 2015;
10 July 2018; 18 February 2021 / Paragraphs
59.1, 236.1, and 311.1 of Annex
and amendments to Annex regarding the deletion of Paragraphs 306
and 512 shall come into force on 20 May 2021. See Paragraph 58 of
the Regulation]
| No. of the synonym of the
substance |
Synonyms of
chemical substances |
No. of the
substance in Annex 1 |
| 1. |
|
abrasive
dust |
543 |
| 2. |
3- |
acetylanisole |
443 |
| 3. |
3- |
acetylmethoxybenzene |
443 |
| 4. |
2- |
acetoxybenzoic acid |
3 |
| 5. |
3-(α- |
acetonylbenzyl)-4- hydroxycoumarin |
651 |
| 6. |
|
adipic
acid dibutyl ester |
165 |
| 7. |
|
adobacillin |
69 |
| 8. |
|
agrimycin |
555 |
| 9. |
|
acrylaldehyde |
17 |
| 10. |
|
acryloilchloride |
16 |
| 11. |
|
acrylic
acid 1H, 1H- tridecafluoroheptyl ester |
602 |
| 12. |
|
acrylic
acid 2-ethoxyethyl ester |
248 |
| 13. |
|
acrylic
acid ethyl ester |
233 |
| 14. |
|
acrylic
acid, heptyl ester |
305 |
| 15. |
|
acrylic
acid methyl ester |
419 |
| 16. |
|
acrofol |
459 |
| 17. |
|
alkanes |
495 |
| 18. |
|
alkyl
amines |
31 |
| 19. |
|
aluminium oxide with silicon dioxide admixture |
369 |
| 20. |
|
amidopyrin |
252 |
| 21. |
1- |
amino-propane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid |
47 |
| 22. |
4- |
amino-1-methoxybenzene |
73 |
| 23. |
2- |
amino-3-(4-imidazolyl) propanoic acid) |
48 |
| 24. |
2- |
amino-3-(2-amino-2-carboxyethyldisulfanyl)propanoic
acid) |
44 |
| 25. |
2- |
amino-3-(3-imidazolyl) propanoic acid) |
58 |
| 26. |
2- |
amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoic acid |
56 |
| 27. |
4- |
amino-3,
5, 6- trichloropyridine-2-carboxylic acid |
32 |
| 28. |
2- |
amino-3-phenyl-propanoic acid |
45 |
| 29. |
2- |
amino-3-guanidinovaleric acid |
41 |
| 30. |
2- |
amino-3-hydroxy-butanoic acid |
57 |
| 31. |
2- |
amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid |
55 |
| 32. |
2- |
amino
-3-mercaptopropionic acid |
43 |
| 33. |
2- |
amino-3-methyl-butanoic acid |
59 |
| 34. |
2- |
amino-3-methyl-pentanoic acid |
49 |
| 35. |
2 - |
amino-4-methylmercaptobutyric acid |
52 |
| 36. |
2- |
amino-4-methyl-pentanoic acid |
50 |
| 37. |
|
aminobenzylpenicillin |
69 |
| 38. |
|
aminobenzene |
72 |
| 39. |
4- |
aminobenzenesulfonamide |
564 |
| 40. |
α - |
amino- β
-phenylpropionic acid |
45 |
| 41. |
α - |
amino- β
-mercaptopropionic acid |
43 |
| 42. |
α - |
amino- β
-.-methylvaleric acid |
49 |
| 43. |
2- |
aminosuccinic acid |
42 |
| 44. |
2- |
aminobenzoate |
108 |
| 45. |
|
aminoacetic acid |
46 |
| 46. |
|
aminophenylmethyl-penicillin |
69 |
| 47. |
α - |
amino-g-methylthiobutyric acid |
52 |
| 48. |
α - |
aminoisocaproic acid |
50 |
| 49. |
ε- |
aminocaproic acid lactam |
366 |
| 50. |
4- |
Amino-N-(3-methoxypyrazin-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide) |
565 |
| 51. |
4- |
amino-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin- 2-yl)-
benzenesulfonamide |
558 |
| 52. |
4- |
amino-N-(5-methoxy-2-pyrimidinyl) benzenesulfonamide |
562 |
| 53. |
4- |
amino-N-(5-ethyl-[1,3,4]thiadiazol-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide |
229 |
| 54. |
4- |
amino-N-(6-methoxy-pyridazin-3-yl)-benzenesulfonamide |
563 |
| 55. |
4- |
amino-N-(aminoiminomethyl)-benzenesulfonamide |
559 |
| 56. |
4- |
Amino-N-(thiazol-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide |
565 |
| 57. |
2- |
aminopropanoic acid |
40 |
| 58. |
3- |
aminopropanoic acid |
18 |
| 59. |
α- |
aminopropionic acid |
40 |
| 59.1 |
4- |
aminotoluene |
598 |
| 60. |
|
ammonium
hydrofluoride |
270 |
| 61. |
|
ammonium
hydrogen phosphate and dihydrogen phosphate mixture |
60 |
| 62. |
|
ammonium
thiocyanate |
64 |
| 63. |
|
antihelmycin |
310 |
| 63.1 |
|
p-anisidine |
73 |
| 64. |
|
apatite |
543 |
| 65. |
|
aziridine |
241 |
| 66. |
|
barium
hydrogen phosphate |
86 |
| 67. |
|
barite |
89 |
| 68. |
|
benzal
chloride |
98 |
| 69. |
|
benzyl
cyanide |
253 |
| 70. |
|
benzo[def]chrysene |
94 |
| 71. |
p- |
benzoquinone |
102 |
| 72. |
1.3- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid |
337 |
| 73. |
1.2- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid anhydride |
281 |
| 74. |
1.2- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid, di-2-propenyl ester |
161 |
| 75. |
1.2- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid, dialkyl esters |
162 |
| 76. |
1.2- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid, dibutyl ester |
167 |
| 77. |
1.2- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid, diethyl ester |
173 |
| 78. |
1.2- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid, dimethyl ester |
202 |
| 79. |
1.4- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid, dimethyl ester |
206 |
| 80. |
1.2- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid, dinonyl ester |
215 |
| 81. |
1.2- |
benzenedicarboxylic acid, diisobutylester |
191 |
| 82. |
1.3- |
benzene-1,3-diol |
525 |
| 83. |
|
benzoic
acid chloroanhydride |
103 |
| 84. |
2,2'- |
bipyridine and 4,4'-bipyridine |
113 |
| 85. |
|
bis(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate |
217 |
| 86. |
|
bis-azepan-1-ylmethanone |
221 |
| 87. |
|
bisphenol A |
341 |
| 88. |
|
bis-N,N'-hexamethylene urea |
221 |
| 89. |
|
bauxite
agglomerate |
543 |
| 90. |
|
boron
trifluoride |
117 |
| 91. |
DL- |
Bornan-2-one |
365 |
| 92. |
1- |
Bromo-3-nitrobenzene |
486 |
| 93. |
1- |
bromobutane |
131 |
| 94. |
|
bromoethane |
236 |
| 95. |
|
bromomethane |
420 |
| 96. |
|
butyraldehyde |
568 |
| 97. |
|
butanal |
568 |
| 98. |
1.4- |
butanedicarboxylic acid |
7 |
| 99. |
1.4- |
butane
dicarbonic acid dibutyl ester |
165 |
| 100. |
1.4- |
butanedicarboxylic acid monoethylester |
8 |
| 101. |
1- |
butanol |
137 |
| 102. |
2- |
butanol |
137 |
| 103. |
n- |
butanol |
137 |
| 104. |
|
butanoic
acid |
567 |
| 104.1 |
|
butanedione |
160.1 |
| 105. |
3- |
butene-2-one |
438 |
| 106. |
1- |
butene-3-yne |
642 |
| 107. |
|
butyl
cellosolve |
139 |
| 108. |
|
butyl
glycol acetate |
140 |
| 109. |
|
butyl
diglycol |
141 |
| 109.1 |
|
1,4-butynediol |
127.1 |
| 110. |
|
cephalosporin N |
142 |
| 111. |
|
cephalosporin P |
142 |
| 112. |
|
cement |
543 |
| 113. |
|
cyanobenzene |
106 |
| 114. |
2- |
cyanoethanol |
309 |
| 115. |
|
cyanoethylene |
11 |
| 116. |
|
cyanomethane |
1 |
| 117. |
|
hardwood |
523 |
| 118. |
p- |
cymol |
154 |
| 119. |
|
zineb |
155 |
| 120. |
|
cis-3-Chloroacrylic acid sodium salt |
459 |
| 121. |
|
cis-3-Chloropropenoic acid, sodium salt |
459 |
| 122. |
|
DBP |
167 |
| 123. |
p,p'- |
DDT
(4,4'-DDT) |
370 |
| 124. |
|
decanedioic acid dibutyl ester |
169 |
| 125. |
|
decanedioic acid dimethyl ester |
203 |
| 126. |
1- |
decanol |
160 |
| 127. |
|
demeton |
407 |
| 128. |
|
desflurane |
71 |
| 129. |
|
dialkyloxalates |
547 |
| 129.1 |
4,4'- |
diaminodiphenylmethane |
427.1 |
| 130. |
1.2- |
diaminoethane |
238 |
| 131. |
1.6- |
diaminohexane |
298 |
| 132. |
2,6- |
diaminohexanoic acid |
51 |
| 133. |
α, ε - |
diaminocaproic acid |
51 |
| 134. |
|
diammonium hydrogen orthophosphate |
60 |
| 135. |
|
diboron
trizinc hexaoxide |
157 |
| 136. |
|
dibromomethane |
427 |
| 137. |
|
diethyl
1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethylpyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
193 |
| 138. |
|
diethylenediamine |
504 |
| 139. |
|
diethyl
((phenylthio)methyl)phosphonate) |
307 |
| 140. |
O,O'- |
diethyl-O''-(2-ethylthioethyl) thiophosphate and
O,O'-diethyl-S-(2-ethylthioethyl) thiophosphate mixture |
407 |
| 141. |
|
diphacinone |
174 |
| 142. |
2- |
diphenylacetyl-1,3-Indandion |
174 |
| 143. |
|
diphenyl |
112 |
| 144. |
|
difluorochlorobromomethane |
121 |
| 145. |
|
diphosphorus pentasulphide |
276 |
| 146. |
|
diphosphorus pentaoxide |
274 |
| 147. |
3.7- |
dihydro-1,3-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
575 |
| 148. |
3.7- |
dihydro-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
576 |
| 149. |
1,3- |
dihydroxybenzene |
525 |
| 150. |
2,2' |
dihydroxydiethyl ether |
171 |
| 151. |
m- |
dichlorobenzol |
183 |
| 152. |
o- |
dichlorobenzol |
182 |
| 153. |
p- |
dichlorobenzol |
184 |
| 154. |
|
dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT) |
370 |
| 154.1 |
|
1,1-dichloroethylene |
645 |
| 155. |
1.2- |
dichloro-1-fluoro-ethane |
267 |
| 156. |
|
dichloromethane |
428 |
| 157. |
|
dichloromethylbenzene |
98 |
| 158. |
α, α - |
dichlorotoluene |
98 |
| 159. |
|
dichromates |
334 |
| 160. |
|
diludine |
193 |
| 161. |
N,N- |
dimethyl-2-hydroxyethylamine |
195 |
| 162. |
2.2- |
Dimethyl-3-(2-methyl-1-propenyl) cyclopropane-1-carboxylic
acid) |
382 |
| 163. |
2.6- |
dimethyl-3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydropyridine |
193 |
| 164. |
2.3- |
dimethylacrylic acid |
415 |
| 165. |
3.3- |
dimethylacrylic acid ethyl ester |
416 |
| 166. |
α, α - |
dimethylbenzylhydroperoxide |
251 |
| 167. |
1.2- |
dimethylbenzene |
386 |
| 168. |
1.3- |
dimethylbenzene |
385 |
| 169. |
1.4- |
dimethylbenzene |
387 |
| 170. |
|
dimethylbenzene |
384 |
| 170.1 |
|
dimethyl
diketone |
160.1 |
| 171. |
N,N- |
dimethylethanolamine |
195 |
| 172. |
N,N- |
dimethylphenylamine |
196 |
| 173. |
1.3- |
dimethylxanthine |
576 |
| 174. |
3.7- |
dimethylxanthine |
575 |
| 175. |
O,O'- |
dimethyl-O''-(2-ethylthioethyl) thiophosphate and
dimethyl-S-(2-ethylthioethyl) thiophosphate mixture |
433 |
| 176. |
2.2- |
dimethylvinylcarbinol |
414 |
| 177. |
2.4- |
dinitrochlorobenzene |
314 |
| 178. |
4.6- |
dinitro-o-cresol |
426 |
| 179. |
2,2'- |
dipyridyl and 4,4'-dipyridyl |
113 |
| 180. |
|
dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether |
441 |
| 181. |
|
disulphur dichloride |
532 |
| 182. |
[10 July 2018] |
| 183. |
3,3'- |
dithiobis-2-aminopropanoic acid |
44 |
| 184. |
1.2- |
dithiodiphosphoric acid, tetraethyl ester |
566 |
| 185. |
|
divanadium pentaoxide smoke |
630 |
| 186. |
|
divanadium trioxide dust |
629 |
| 187. |
|
DNOC |
426 |
| 188. |
|
dodecan-1-ol |
220 |
| 189. |
|
dolomite |
543 |
| 190. |
|
DPM |
441 |
| 191. |
|
yellow
prussiate of potash |
358 |
| 192. |
|
iron
agglomerate |
223 |
| 193. |
|
baking
soda |
461 |
| 194. |
|
electro-corundum |
22 |
| 195. |
|
enflurane |
71 |
| 196. |
1.2- |
epoxypropane |
518 |
| 197. |
2- |
propenoic acid 2-ethoxyethyl ester |
248 |
| 198. |
|
ethanal |
2 |
| 199. |
N,N'- |
ethanediylbis-dithiocarbamic acid zinc salt |
155 |
| 200. |
1.2- |
ethanediol |
239 |
| 201. |
|
ethanedioic acid |
546 |
| 202. |
|
ethanol |
246 |
| 203. |
|
acetic
acid 3-methylbutyl ester |
335 |
| 204. |
|
acetic
acid, benzyl ester |
96 |
| 205. |
|
acetic
acid, methyl ester |
418 |
| 206. |
|
acetic
acid, propyl ester |
513 |
| 207. |
|
acetic
acid, vinyl ester |
641 |
| 208. |
|
ethyl
-[[3-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl]oxy]acetate
hydrochloride |
368 |
| 209. |
|
crotonic
acid, 3-methyl-, ethyl ester |
416 |
| 210. |
|
ethyl
acetate |
232 |
| 211. |
|
ethylbutylcetone |
304 |
| 211.1 |
|
ethylene
dichloride |
186 |
| 212. |
1.2- |
ethylendicarbonic acid anhydride |
400 |
| 213. |
|
ethylene
glycol dimethyl ether |
207 |
| 214. |
|
ethyleneglycol monobutyl ether acetate |
140 |
| 215. |
|
ethyleneglycol monobutyl ether |
139 |
| 216. |
|
ethylene
glycol monoethyl ether |
237 |
| 216.1 |
|
2-ethyl-1-hexanol |
243.1 |
| 217. |
2- |
ethylhexyl acrylate |
14 |
| 217.1 |
|
2-ethylhexyl alcohol |
243.1 |
| 218. |
|
ethylsoamykeltone |
423 |
| 219. |
|
ethyl
mercaptan |
228 |
| 220. |
|
ethylmethylketone |
126 |
| 221. |
O- |
ethyl
O-phenyl S-propyl phosphorothioate |
307 |
| 221.1 |
|
ethyl
silicate |
579.1 |
| 222. |
2- |
ethoxyethanol |
237 |
| 223. |
|
phenibute |
33 |
| 224. |
[(2- |
phenyl-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2.3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methyl-amino]
methan
esulfonate |
70 |
| 225. |
6- |
phenylacetamido penicillinic acid sodium salt |
99 |
| 226. |
|
phenylamine |
72 |
| 227. |
2- |
phenylazomalononitrile |
254 |
| 228. |
N,N'-(m- |
phenylene) disuccinimide |
258 |
| 229. |
1,1-(1,3- |
phenylene)bis(1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione) |
258 |
| 230. |
1.2- |
phenylenediamine |
256 |
| 231. |
1.3- |
phenylenediamine |
255 |
| 232. |
1.4- |
phenylenediamine |
257 |
| 232.1 |
|
Phenylene ether |
175.1 |
| 233. |
|
phenylhydrazonomalononitrile |
254 |
| 234. |
|
phenylcarbinol |
100 |
| 235. |
|
phenylmethanol |
100 |
| 236. |
|
phenyl
methyl ketone |
4 |
| 236.1 |
2- |
phenylpropane |
388 |
| 237. |
2- |
phenylpropene |
436 |
| 238. |
|
phenmedipham |
111 |
| 238.1 |
|
Phenoxybenzene |
175.1 |
| 239. |
3- |
phenoxyphenol |
262 |
| 240. |
|
ferro-vanadium |
631 |
| 241. |
|
phytomycin |
555 |
| 242. |
|
phlogopite |
543 |
| 243. |
|
formaldehyde dimethylacetal |
208 |
| 244. |
2- |
formylfuran |
288 |
| 245. |
|
phosphorus pentachloride |
273 |
| 246. |
|
phosphorus pentaoxide |
274 |
| 247. |
|
phosphoryl trichloride |
275 |
| 248. |
|
phosphoric acid, dibutyl phenyl ester |
166 |
| 249. |
|
freon
11 |
268 |
| 250. |
|
freon
12 |
177 |
| 251. |
|
freon 12
Br |
121 |
| 252. |
|
freon 13
B1 |
124 |
| 253. |
|
freon
141 |
267 |
| 254. |
|
freon
142 |
179 |
| 255. |
|
freon
143 |
609 |
| 256. |
|
freon
152 |
178 |
| 257. |
|
freon
-112 |
176 |
| 258. |
2- |
furancarboxaldehyde |
288 |
| 259. |
|
germanium (IV) oxide |
292 |
| 260. |
|
germane |
293 |
| 261. |
|
glutamic
acid 5-lactam |
53 |
| 262. |
|
glutaric
acid dialdehyde |
294 |
| 263. |
|
grain
dust |
523 |
| 263.1 |
|
gypsum
dust |
353.1 |
| 264. |
|
halotan |
71 |
| 265. |
|
hexachloropropanone |
295 |
| 266. |
1.6- |
hexanediamine |
298 |
| 267. |
1.6- |
hexamethylene diisocyanate |
299 |
| 268. |
|
hexanedioic acid dibutyl ester |
165 |
| 269. |
|
hexanoic
acid |
367 |
| 270. |
|
heptanol |
306 |
| 271. |
|
herban |
289 |
| 271.1 |
|
hydrogenated diphenylbenzenes |
308.1 |
| 272. |
2- |
hydroxy-2-methylpropionitrile |
5 |
| 273. |
(R)-4- |
hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-butyl))-2-benzopyrone |
651 |
| 274. |
(S)-4- |
hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-butyl))-2-benzopyrone |
651 |
| 275. |
7-[2- |
hydroxy-3-(N-(2-hydroxyethyl), -N-methylamino] propyl)
theophylline nicotinate |
383 |
| 276. |
|
hydroxybenzene |
264 |
| 277. |
2- |
hydroxybenzoato-lead salt |
570 |
| 278. |
2- |
hydroxyethyl acrylate |
15 |
| 279. |
3-(4- |
hydroxyphenyl)alanine |
56 |
| 280. |
α- |
hydroxyisobutyronitrile |
5 |
| 281. |
2- |
hydroxymethylfuran |
287 |
| 282. |
1- |
hydroxynaphthalene |
456 |
| 283. |
2- |
hydroxynaphthalene |
457 |
| 284. |
3- |
chloro-1,2-epoxypropane |
226 |
| 284.1 |
1- |
chloro-2,3-epoxypropane |
226 |
| 285. |
1- |
chloro-3-hydroxypropane |
312 |
| 286. |
|
chloroacetyl chloride |
447 |
| 287. |
|
chloral |
612 |
| 288. |
|
picloram |
32 |
| 289. |
1- |
chlorobutane |
133 |
| 290. |
|
chloroethane |
244 |
| 291. |
|
chloroacetic acid |
446 |
| 292. |
|
chloroethylene |
644 |
| 293. |
|
chloromethane |
429 |
| 294. |
|
chloropon |
618 |
| 295. |
|
chloropelargonic acid |
319 |
| 296. |
α - |
chloropropionic acid |
322 |
| 297. |
α - |
chlorotoluene |
97 |
| 298. |
|
homopiperidine |
300 |
| 299. |
|
chromium
orthophosphate |
328 |
| 300. |
|
chromium
trioxide |
329 |
| 301. |
|
chromium-ammonium alum |
333 |
| 302. |
|
intencordin |
368 |
| 303. |
|
Iintensain |
368 |
| 304. |
|
slag and
mineral wool |
543 |
| 305. |
|
isoamyl
methyl ketone |
422 |
| 306. |
[18 February
2021. See Paragraph 58 of Amendments] |
| 307. |
|
isobutyl
acetone |
422 |
| 308. |
|
isobutyl
methyl ketone |
424 |
| 309. |
|
iso-butyl alcohol |
137 |
| 310. |
|
isoflurane |
71 |
| 311. |
[7 April 2015] |
| 311.1 |
|
isopentyl alcohol |
336 |
| 312. |
|
isopentyl acetate |
335 |
| 313. |
|
isopentyl methyl ketone |
422 |
| 314. |
|
isopropylbenzene |
250 |
| 315. |
|
isopropyl acetate |
424 |
| 316. |
|
isopropylbenzene hydroperoxide |
251 |
| 317. |
|
isopropylbenzene |
388 |
| 318. |
|
isopropyl alcohol |
340 |
| 319. |
2- |
isopropyltoluene |
154 |
| 320. |
3- |
isopropyltoluene |
154 |
| 321. |
4- |
isopropyltoluene |
154 |
| 322. |
|
calcium
dihydroxide |
348 |
| 323. |
|
dipotassium hexafluorosilicate |
357 |
| 324. |
|
potassium O- alkyldithiocarbonate |
354 |
| 325. |
|
Carbonic
acid, dithio-, O-butyl ester |
355 |
| 326. |
|
Potassium O-ethyl dithiocarbonate |
356 |
| 327. |
|
carbamonitrile |
148 |
| 328. |
|
carbathione |
466 |
| 329. |
|
carbinol |
413 |
| 330. |
|
carboxide (pesticide) |
221 |
| 331. |
1- |
carboxymethyl pyridinium betaine |
111 |
| 332. |
|
carbonyl
dichloride |
280 |
| 333. |
|
caustic
soda |
462 |
| 334. |
|
pottery |
543 |
| 335. |
|
cresol
mixture |
381 |
| 336. |
|
trisodium hexafluoroaluminate |
270 |
| 337. |
2.6- |
xylenol |
200 |
| 338. |
o-,m-,p- |
xylene |
384 |
| 339. |
|
cumyl
hydroperoxide |
251 |
| 340. |
|
cumene
hydroperoxide |
251 |
| 341. |
|
cumolhydroperoxide |
198 |
| 342. |
|
cuprozan |
155 |
| 343. |
|
white
spirit |
393 |
| 344. |
|
lauryl
alcohol |
220 |
| 345. |
|
luminophores P - 385 |
84 |
| 346. |
|
magnesium dodecaboride |
398 |
| 347. |
|
maleinanhydride |
400 |
| 348. |
|
clay |
543 |
| 349. |
|
maneb |
404 |
| 350. |
|
methacrylic anhydride |
410 |
| 351. |
|
methacrylic chloride |
411 |
| 352. |
|
methanal |
271 |
| 353. |
|
methanoic acid |
548 |
| 354. |
2- |
metyl-1,3-butadiene |
339 |
| 355. |
3- |
metyl-1-butanol |
336 |
| 356. |
1- |
methyl-1-ethanol |
340 |
| 357. |
2- |
Methyl-propan-1-ol |
137 |
| 358. |
3- |
methyl-2-butanol |
431 |
| 359. |
|
methyl
2-methylpropenoate |
434 |
| 360. |
N- |
Methyl2-pyrrolidone |
425 |
| 361. |
2- |
Methyl-propan-2-ol |
137 |
| 362. |
|
methyl-amyl-ketone |
303 |
| 363. |
|
methylal |
208 |
| 364. |
|
methylbenzol |
600 |
| 365. |
3- |
methyl-1-butyl acetate |
335 |
| 366. |
1- |
methylbutyl ethanoate |
421 |
| 366.1 |
|
demeton-methyl |
433 |
| 367. |
|
methyldithiocarbamate |
466 |
| 368. |
|
methyldithiocarbamic acid, sodium salt |
466 |
| 369. |
|
methylethylketone |
126 |
| 370. |
o-, m-, p- |
methylphenols |
381 |
| 371. |
|
methyl
chloroform |
605 |
| 372. |
|
methylisobutylketone |
424 |
| 373. |
2- |
Crotonic
acid, 2-methyl- |
415 |
| 374. |
|
methyl
mercaptan |
412 |
| 375. |
4- |
methyl-m-phenylene diisocyanate |
599 |
| 376. |
|
methyloxirane |
518 |
| 377. |
|
methyl
pentyl ketone |
303 |
| 378. |
4- |
methylpiperazine-1amine |
34 |
| 379. |
3-(1- |
Methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl) pyridine |
474 |
| 380. |
|
methyl
propenoate |
419 |
| 381. |
2- |
methylpropionic acid |
409 |
| 382. |
2- |
methylpropenoic acid anhydride |
410 |
| 383. |
2- |
methylpropionic acid amide |
408 |
| 384. |
2- |
propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, butyl ester |
135 |
| 385. |
2- |
methylpropenoic acid chloroanhydride |
411 |
| 386. |
2- |
methyl-2-propenoic acid methyl este |
433 |
| 387. |
|
methyl
alcohol |
413 |
| 388. |
α- |
methylstyrene |
250 |
| 389. |
N- |
Methylurea |
437 |
| 390. |
1- |
methoxy-4-nitrobenzene |
484 |
| 391. |
4- |
methoxyaniline |
73 |
| 392. |
5- |
methoxysulfadiazine |
562 |
| 393. |
|
monoethanolamine |
35 |
| 394. |
|
monochlorbenzene |
317 |
| 395. |
|
monopropylene glycol methyl ether |
442 |
| 396. |
|
muscovite |
543 |
| 397. |
|
petroleum |
393 |
| 398. |
2- |
naphthenic acid |
453 |
| 399. |
α - |
naphthol |
456 |
| 400. |
β |
naphthol |
457 |
| 401. |
|
sodium
3-chloroacrylate |
459 |
| 402. |
|
soda
lye |
462 |
| 403. |
|
sodium
thiocyanate |
470 |
| 404. |
|
n-butyl
acetate |
231 |
| 405. |
|
inorganic chromium (II) compounds |
327 |
| 406. |
|
inorganic chromium (III) compounds |
327 |
| 407. |
|
nicotinamide |
476 |
| 408. |
N-(5- |
Nitro-2-furfurylidene)-1-aminohydantoin |
284 |
| 409. |
m- |
nitroaniline |
482 |
| 410. |
o- |
nitroaniline |
481 |
| 411. |
p- |
nitroaniline |
483 |
| 412. |
|
nitrofural |
282 |
| 413. |
|
nitrofurantoin |
283 |
| 414. |
3-(5- |
nitrofurfurylidenamino)-2-oxazolidinone |
286 |
| 415. |
5- |
nitrofuranyl semicarbazone |
282 |
| 416. |
N-[2-(5'- |
nitrofuryl-2)-2-propenylidine]-1-amino-hydantoin |
284 |
| 417. |
N-[(5'- |
nitro-2'-furyl)acrylidene]-1-aminohydantoin |
284 |
| 417.1 |
|
nitroglycerin |
293.1 |
| 418. |
|
nivalin |
289 |
| 419. |
|
nonanol |
491 |
| 420. |
|
norsulfazole |
565 |
| 421. |
|
nururon |
289 |
| 422. |
|
carbon
disulphide |
533 |
| 423. |
|
carbon
monoxide |
493 |
| 424. |
|
carbon
tetrafluoride |
587 |
| 425. |
2,2' |
oxybisethanol |
171 |
| 426. |
|
oxirane |
242 |
| 427. |
2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5 |
octafluoropenthyl acrylate |
13 |
| 428. |
|
octan-1,8-dicarboxilic acid dioctyl ester |
217 |
| 429. |
1.8- |
octane
dicarboxylic acid |
528 |
| 430. |
1.8- |
octane-1,8-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester |
203 |
| 431. |
|
octanol |
497 |
| 432. |
|
orthoboric acid barium salt |
83 |
| 433. |
|
orthophosphoric acid |
278 |
| 434. |
|
pemza |
543 |
| 435. |
|
3-Penten-3-ol |
414 |
| 436. |
|
pentacarbonyliron |
222 |
| 437. |
1.5- |
pentanedial |
294 |
| 438. |
1- |
pentanol |
30 |
| 439. |
|
pentanoic acid |
79 |
| 440. |
3- |
pentyl
acetate |
26 |
| 441. |
|
pentyl
acetate |
25 |
| 442. |
|
pentyl
bromide |
28 |
| 443. |
3- |
pentyl
ethanoate |
26 |
| 444. |
|
pentyl
ethanoate |
25 |
| 445. |
|
pentyl
formate |
29 |
| 446. |
|
perhydroazepine |
300 |
| 447. |
|
perchloroethylene |
586 |
| 448. |
|
perlite |
543 |
| 449. |
|
petroleum ether |
392 |
| 450. |
|
polyethylene |
510 |
| 451. |
|
piramidon |
252 |
| 452. |
|
pyrethrum |
506 |
| 453. |
1- |
pyridylacetic acid betaine |
111 |
| 454. |
|
pyridine-3-carboxylic acid |
475 |
| 455. |
|
pyridine-3-carboxylic acid amide |
476 |
| 456. |
|
pyrimidine-4,5,6-triamino sulphate |
601 |
| 457. |
|
pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic acid |
53 |
| 458. |
2- |
pyrrolidone carboxylic acid |
54 |
| 459. |
|
polyamide |
510 |
| 460. |
|
polyethylene terephtalate |
389 |
| 461. |
|
polyformaldehyde |
510 |
| 462. |
|
polycaprolactam |
510 |
| 463. |
|
polypropylene |
510 |
| 464. |
|
polysaccharide |
390 |
| 465. |
|
polyurethane |
510 |
| 466. |
|
Portland
cement |
144 |
| 467. |
|
propanal |
522 |
| 468. |
1.2- |
Propanediol cyclic carbonate |
515 |
| 469. |
1.2- |
propanediol |
517 |
| 470. |
1- |
propanol |
521 |
| 471. |
2- |
propanol |
342 |
| 472. |
2- |
propanone |
6 |
| 473. |
2- |
propanol, dimethyl ketone |
6 |
| 474. |
|
propionic acid propyl ester |
520 |
| 475. |
2- |
propene-1-ol |
19 |
| 476. |
2- |
prop-2-enal |
17 |
| 477. |
|
propenoyl chloride |
16 |
| 478. |
|
propene |
519 |
| 479. |
|
propenoic acid |
12 |
| 480. |
2- |
propenoic acid 2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,7-tridecafluoroheptyl
ester |
602 |
| 481. |
2- |
propenoic acid 2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5-octafluoropenthyl ester |
13 |
| 482. |
2- |
propenoic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester |
14 |
| 483. |
|
propenoic acid 2-hydroxyethyl ester |
240 |
| 484. |
|
propenoic acid amide |
10 |
| 485. |
2- |
propenoic acid ethyl ester |
233 |
| 486. |
|
propenoic acid, heptyl ester |
305 |
| 487. |
|
propenoic acid, methyl ester |
419 |
| 488. |
n- |
propylamine |
514 |
| 489. |
|
propylbenzene |
388 |
| 490. |
|
propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate |
441 |
| 491. |
|
propylene glycol monomethyl ether |
442 |
| 492. |
|
propylene chlorohydrin |
315 |
| 493. |
2- |
propyn-1-ol |
511 |
| 494. |
|
propionic acid |
512 |
| 495. |
|
pseudocumol |
623 |
| 496. |
|
dust of
plant and animal origin |
523 |
| 497. |
|
dust,
sugar |
523 |
| 498. |
|
dust,
wood |
523 |
| 499. |
|
cotton,
linen, wool, piles, and peat dust |
523 |
| 500. |
|
dust,
flour |
523 |
| 500.1 |
|
carbon,
coal, diamond dust |
494 |
| 501. |
|
dust,
paper |
523 |
| 501.1 |
|
polymeric materials (polyethylene, polypropylene etc.)
dust |
510 |
| 501.2 |
|
silicate
and aluminosilicate dust |
543 |
| 502. |
|
dust,
tobacco |
523 |
| 503. |
|
dust of
talc type |
523 |
| 504. |
|
tea
dust |
523 |
| 505. |
|
ratindan |
174 |
| 506. |
|
rimactane |
527 |
| 507. |
|
salycilic acid cupric salt |
636 |
| 508. |
|
red
prussiate of potash |
359 |
| 509. |
|
sebacic
acid dibutyl ester |
169 |
| 510. |
|
sebacic
acid, dimethyl ester |
203 |
| 511. |
|
sebacic
acid dioctyl ester |
217 |
| 512. |
[18 February 2021 /
See Paragraph 58 of the Regulation] |
| 513. |
|
sulphur
dioxide |
530 |
| 514. |
|
sulphur
trioxide |
531 |
| 515. |
|
sulphuric anhydride |
531 |
| 516. |
|
sevoflurane |
71 |
| 516.1 |
|
formic
acid methyl ester |
421.1 |
| 517. |
|
formic
acid pentyl ester |
29 |
| 518. |
|
glass
fibre |
543 |
| 519. |
|
glass
wool |
543 |
| 520. |
|
streptocide |
564 |
| 521. |
|
sulfodimesin |
558 |
| 522. |
|
sulfaethylthiadiazole |
229 |
| 523. |
|
sulfaethidiole |
229 |
| 524. |
|
sulphamethazine |
558 |
| 525. |
|
sulfanilylguanidine |
559 |
| 526. |
|
sulphanilic acid 6-methoxy-3-pyridazinyl amide |
563 |
| 527. |
|
sulphanilic acid thiazol-2-ylamide |
565 |
| 528. |
|
sulfanilcarbamide |
637 |
| 529. |
|
sulgin |
559 |
| 530. |
|
talc |
543 |
| 531. |
|
theophylline + 1,2 ethylenediamine |
225 |
| 532. |
|
tert-butanol |
137 |
| 533. |
|
tert-pentyl acetate |
27 |
| 534. |
|
tert-Pentyl hydroperoxide |
417 |
| 535. |
|
terylene |
389 |
| 535.1 |
|
tetraethoxysilane |
579.1 |
| 536. |
|
tetraboron silicide |
541 |
| 537. |
|
tetraethyldithiopyrophosphate |
566 |
| 538. |
|
tetrafluoro-1,3-dichloroacetone |
581 |
| 539. |
|
tetrachlorodifluoroethane |
176 |
| 540. |
|
tetracarbonyl nickel |
479 |
| 541. |
|
tillam |
245 |
| 542. |
|
TNT |
624 |
| 543. |
m- |
tolylene
diisocyanate |
599 |
| 544. |
|
toluene-2,3- diamine |
163 |
| 545. |
|
toluene-2,4-diisocyanate |
599 |
| 546. |
|
tordon-22k |
32 |
| 547. |
|
triacylglycerol |
394 |
| 547.1 |
|
1,2,4-triazol-3-amine |
30.1 |
| 548. |
|
trizinc
diphosphide |
156 |
| 549. |
|
trifluorobromomethane |
124 |
| 550. |
1,1,1- |
bis-(4-chlorophenyl)-2,2,2,-trichloroethane |
370 |
| 551. |
|
trichloroethene |
615 |
| 552. |
|
trichloromethane |
320 |
| 553. |
|
tricarbonyl (methylcyclopentadienyl) manganese |
403 |
| 554. |
|
trimellitic acid |
105 |
| 555. |
1,3,5- |
trimethylbenzene |
445 |
| 556. |
1,7,7- |
trimethylbicyclo(2,2,1)heptan-2-one |
365 |
| 557. |
|
trimethylene chlorohydrin |
312 |
| 558. |
1,3,7- |
trimetylxanthine |
375 |
| 559. |
2,4,6- |
trinitrophenol |
503 |
| 560. |
|
trisilicon tetranitride |
540 |
| 561. |
|
tricopper phosphide |
633 |
| 562. |
|
tuff |
543 |
| 562.1 |
|
carbon
monoxide gas |
493 |
| 563. |
|
white
spirit |
393 |
| 564. |
|
warfarin |
651 |
| 565. |
|
vinylbenzene |
554 |
| 566. |
|
vinylbenzene |
435 |
| 567. |
N- |
vinylpyrrolidone |
640 |
| 568. |
|
vinyltoluene |
435 |
| 569. |
|
vitamin
B2 |
526 |
| 570. |
|
mica |
543 |
| 571. |
|
hydrocyanic acid |
149 |
Acting for the Minister for
Welfare,
Minister for the Environment R. Vējonis
In Revised
Version Submitted by the Ministry of Welfare
Annex 3
Cabinet
Regulation No. 325
15 May 2007
Biological Limit Values
[18 February 2021 / The new
wording of Annex shall come into force on 11 July 2021. See
Paragraph 59 of the Regulation]
1. The BLV of lead (Pb):
1.1. in blood is 30 µg Pb/100 ml (reference value - lead
concentration in blood of population not subject to occupational
exposure ≤ 10 µg/100 ml). A repeat blood test shall be carried
out in two months if the lead level is 30-60 µg/100 ml. If the
lead level is > 60 µg/100 ml, transfer to work where there is
no contact with lead, health care and a repeat control of Pb
level are required;
1.2. clinical blood picture, reticulocytes and punctate
graininess of basophils in erythrocytes;
1.3. coproporphyrin in urine -100 µg/g of creatinine
(reference value 22-57 µg/g of creatinine);
1.4. aminolevulinic acid in urine - 5 mg/g of creatinine
(reference value 0.5-2.5 mg/g of creatinine).
2. The BLV of mercury (Hg):
2.1. in blood is 10 µg Hg/L (reference value for the mercury
concentration in blood of population not subject to occupational
exposure < 1 µg/L);
2.2. in urine is 30 µg Hg/g creatinine (reference value for
the mercury concentration in urine is < 5 µg Hg/g creatinine
or 3.5 µg/L).
3. The BLV of cadmium (Cd) in urine is 2 µg Cd/g creatinine
(the time of taking samples does not affect the results of
analyses).
4. The BLV of chromium (Cr) in urine is 10 µg Cr/g creatinine
when changing during a shift, the urine samples are taken at the
end of the shift or working week (reference value of the total
chromium concentration in blood of population not subject to
occupational exposure < 0.8 µg/L, in urine - < 0.01
µmol/L).
5. Metabolites and the following chemical substances shall be
determined to organic solvents (benzene, toluene, styrene):
5.1. to benzene - phenylmercapturic acid (BLV 46 µg/g
creatinine) shall be determined in urine at the end of the shift
or exposure, benzene (BLV 28 µg/L) shall be determined in blood
immediately after the end of the shift;
5.2. to toluene - hippuric acid shall be determined in urine
(BLV 1.6 g/g creatinine) at the end of the shift, in blood -
toluene (BLV 0.05 mg/L);
5.3. to styrene - mandelic acid shall be determined in urine
(BLV 0.8 g/g creatinine) at the end of the shift, in blood -
styrene (BLV 0.55 mg/L).
6. The activity of cholinesterase in erythrocytes shall be
determined to phosphorus organic compounds, BLV 70 % of the base
level.
7. The BLV for aniline in urine is 0.2 mg aniline/L (after
hydrolysis, the urine samples have been taken at the end of the
shift).
8. The BLV for cumene (2-phenylpropane) in urine is 7 µg
2-phenyl-2-propanol/g creatinine, the urine samples have been
taken within two hours after the end of the shift.
9. The BLV for nickel and its inorganic compounds in urine is
3 µg Ni/L.
In Revised
Version Submitted by the Ministry of Welfare
Annex 4
Cabinet
Regulation No. 325
15 May 2007
Determination of Concentration of
a Chemical Substance in the Air of the Working Environment
1. Samples shall be taken in the more characteristic
workplaces. Performing the same work operation with similar
tools, the air of the working environment shall be controlled by
the sampling principle of workplaces, choosing them both in the
centre of the room and at the sides of the room.
2. The air for analysis shall be taken during the working
process (in typical work conditions) in the zone of breathing of
the employee - in the hemisphere of the part of the room within
0.3 m radius, which embraces the face of a human with a centre in
the middle between the eyes and the centre of which is situated
on the line which goes through the middle of the head and
larynx.
3. During the shift or during a separate stage of the
technological process at one workplace (point) at least three
samples shall be taken for the assessment of exposure; in
determining aerosols of fibrogenic effect, one sample is
permissible.
4. Calibrated accurate instrumental analytical measuring
equipment shall be used for sampling and analysis.
5. If the gas and vapour concentration (Cg) is
expressed in measurement units independent from temperature and
air pressure ppm, then taking into account the molar weight of
the substance [vielas molmasa] and the capacity taken by the mol
of the gaseous substance at the relevant temperature, the
concentration of the mass of the gaseous chemical substance (C,
mg/m3) shall be calculated in accordance with the
following formulae:
| C(mg / m3) = |
molar weight of the substance |
x Cg(ppm), at 20°C |
| 24.04 |
| C(mg / m3) = |
molar weight of the substance |
x Cg(ppm), at 25°C |
| 24.44 |
6. Expressing the concentration of the mass of the gaseous
chemical substance (C, mg/m3) as the gas and vapour
concentration (Cg) in measurement units independent
from temperature and air pressure ppm, the following
recalculation formulae shall be used:
|
Cg(ppm) = |
24.04 |
x C(mg /
m3), at 20°C |
| molar weight of the substance |
|
Cg(ppm) = |
24.44 |
x C(mg /
m3), at 25°C |
| molar weight of the substance |
7. The concentration of the chemical substance for the shift
shall be determined in the following way:
7.1. one or several consecutive air samples shall be taken
during the eight hour working day or during a shift (the amount
of air of the working environment, which is taken for analysis in
order to measure the concentration of dangerous substances in the
air sample taken), in which the necessary analyses are
performed;
7.2. sampling shall be performed using individual air
receivers (devices which receive air at the respiration area of
the employee), during the shift or the average indicator is
determined after the results of analysis taken separately during
the shift;
7.3. in determining the average indicator by the results of
analysis taken separately during the shift, it shall be
calculated as the average for a time period, when the employee
performs all the operations of the technological process; and
7.4. the calculations of the concentration shall be performed
in accordance with the following formula:
|
Cmaiņā = |
∑ Ci ti |
= |
C1 t1 + C2
t2 + ········Cn
tn |
, where: |
| ∑ ti |
8 |
Cmaiņā - indicates the average arithmetical
concentration of the chemical substance during the shift,
mg/m3;
Ci, C1,C2 …Cn- the
concentration of the dangerous chemical substance in time periods
of separate stages of the technological process (operations) ,
mg/m3 during the shift;
ti, t1 , t2, tn -
the duration of separate stages (operations) of the technological
process - the corresponding exposure time, expressed in hours
∑ti - the duration of the whole shift in hours, for
example, 8 hours;
7.5. the assessment of the working environment shall cover at
least 75 % of the duration of a shift and it shall be performed
during several work shifts.
8. Specification of the concentration of the chemical
substance in the samples obtained during the performance of
measurements shall be carried out in accordance with the method
used in a certain case and the measurement instrument and the
results obtained shall be compared with OEV.
9. In determining the concentration of dangerous chemical
substances:
9.1. the methodology and measurement instruments for
specification of chemical substances shall ensure specific
substance specification even if other substances are present in
the working environment at least at 0.1 OEV level (for
specification of the approximate concentration 0.5 OEV level is
permissible);
9.2. the total error of the concentration of the chemical
substance may not exceed ± 25 %;
9.3. the result of the measurement of the chemical substance
concentration shall be applied to circumstances where the air
temperature is 20 0C (293 K) and ambient pressure 760
mm Hg (101,23 kPa).
10. Specification of the approximate concentration of chemical
substances with indication tubes and other indicative measurement
instruments shall be performed in accordance with the information
provided by the manufacturer, including operating instructions,
taking into account the presence of other substances in the air
of the working environment at the same time and the possible
effect thereof on the results of measurements;
11. Quick operation gas analysers shall be used for continuous
automated control of dangerous substances of quick exposure in
the working environment.
12. If the result below the detection limit of the method (the
minimum concentration of the chemical substance, which may be
detected using this method) is obtained during measurements, it
shall be considered that the concentration of the chemical
substance to be determined is a half of the concentration of such
chemical substance, which is specified as a detection limit of a
particular method.
Acting for the Minister for
Welfare,
Minister for the Environment R. Vējonis
Translation © 2021 Valsts valodas centrs (State
Language Centre)




