Text consolidated by Valsts valodas centrs (State
Language Centre) with amending regulations of:
15 April 2008 [shall come
into force from 19 April 2008];
13 October 2009 [shall come into force from 21 October
2009];
20 September 2011 [shall come into force from 24
September 2011];
27 March 2012 [shall come into force from 1 April
2012];
8 January 2013 [shall come into force from 1 February
2013];
10 December 2013 [shall come into force from 1 January
2014];
25 November 2014 [shall come into force from 1 January
2015];
29 September 2015 [shall come into force from 3 October
2015];
16 February 2016 [shall come into force from 1 March
2016].
If a whole or part of a paragraph has been amended,
the date of the amending regulation appears in square
brackets at the end of the paragraph. If a whole
paragraph or sub-paragraph has been deleted, the date of
the deletion appears in square brackets beside the
deleted paragraph or sub-paragraph.
|
Republic of Latvia
Cabinet
Regulation No. 265
Adopted 4 April 2006
|
Procedures for Keeping Medical
Documents
[20 September
2011]
Issued pursuant to
Section 59 of the Medical Treatment Law
I. General Provisions
1. This Regulation prescribes the procedures for keeping
medical documents in medical treatment institutions (hereinafter
- the document keeping procedures).
[20 September 2011]
2. The document keeping procedures shall be binding on all
medical treatment institutions of the Republic of Latvia.
3. The document keeping procedures shall be a part of the
mandatory requirements defined for a medical treatment
institution.
[13 October 2009]
4. The implementation of this Regulation shall be controlled
by the Health Inspectorate.
[15 April 2008]
II. Entries in Medical and
Register Documentation
5. Medical documents regarding receipt of a primary health
care, secondary health care and emergency medical assistance
(hereinafter - the medical entries) shall form a unified
information unit. The medical entries shall be compiled and
stored by a general practitioner (a primary health care
internist, a primary health care pediatrist). The medical entries
shall be electronically accumulated in a unified electronic
information system of the health sector in accordance with the
laws and regulations regarding the unified electronic information
system of the health sector.
[10 December 2013 / New wording of
this Paragraph shall come into force on 1 April 2014.]
6. If a patient changes the general practitioner (the primary
health care internist, the primary health care pediatrist), the
general practitioner shall transfer the complete medical entries
regarding the relevant patient to the general practitioner
selected by the patient.
7. The medical entries made regarding a patient in an
out-patient medical treatment institution shall form an
out-patient medical card of the patient. The medical entries
regarding a patient made in an inpatient medical treatment
institution shall form the medical history of the patient.
8. The doctor providing medical treatment shall append to the
medical entries of a patient information regarding a health care
service provided to a patient which is received in other medical
treatment institution or which is provided by other medical
treatment persons.
9. The medical entries of patients discharged from an
inpatient medical treatment institution shall be completed and
transferred for storage to a filing cabinet of the inpatient
medical treatment institution not later than 14 days after the
discharge from the inpatient medical treatment institution. A
responsible medical practitioner assigned by the head of the
inpatient medical treatment institution shall be responsible for
the transfer of the medical entries for storage to the filing
cabinet of the inpatient medical treatment institution.
9.1 The medical entries regarding health care at
home shall be completed and transferred for storage to a filing
cabinet of the inpatient medical treatment institution within
seven days after completion of the home care episode.
[20 September 2011]
III. Content and Protection of the
Medical Entries
10. The medical entries shall contain information which
ensures recognition of a patient, certifies diagnosis,
substantiates examinations and medical treatment methods, and
also precisely demonstrates medical treatment results.
[15 April 2008]
11. The medical entries, which are to be competed in an
inpatient medical treatment institution, shall also be completed
by outpatient medical treatment institutions, if surgical
operations or manipulations have been carried out in the
outpatient operation ward of the day hospital of the relevant
institution.
12. An evolution of the disease shall be entered in the
medical entries within 24 hours after the patient's reception in
an inpatient medical treatment institution.
13. If additional information regarding any activity related
to medical treatment, manipulation and pre-operational time of a
patient is obtained or submitted, it shall be added to the
medical entries without delay.
14. An opinion on completion of hospitalisation may be
replaced by a final entry, which contains information regarding
medical treatment results and recommendations, if:
14.1. the patient must be hospitalised for a period of less
than 48 hours;
14.2. a healthy child is born in labour and labour has
occurred without complications.
14.1 Epicrisis regarding health care at home shall
be completed in two copies, if the health care at home or episode
thereof is finished. One copy shall be transferred to the general
practitioner of the patient, the other copy shall be appended to
the patient's medical card.
[20 September 2011]
15. If the death of a patient has occurred, an opinion on the
death and a final entry, in which the reason due to which the
patient has been received in a hospital (if a patient has died in
the hospital), the results of examinations and medical treatment
course, and also reasons of the death shall be provided, shall be
added to the medical entries.
16. If an autopsy is carried out after the death of a patient,
a pathological anatomical diagnosis shall be appended to the
medical entries within three days, but a complete statement shall
be appended to the medical entries within 30 days after the
autopsy.
17. A summary is one of the parts of the medical entries of
the outpatient medical treatment institution. The summary shall
contain the following information:
17.1. the final diagnosis;
17.2. information regarding diseases (also infectious
diseases) and injuries (according to a patient's words) suffered
previously;
17.3. known significant surgical and invasive procedures;
17.4. known adverse and allergic reactions;
17.5. information regarding medicinal products to be used on
regular basis.
18. The summary shall be located in an outpatient medical card
of a patient at the same place. It shall be completed in the case
of the first time illness and in the case of acute condition of a
chronic illness, or when a patient visits a medical practitioner
for the first time. Hereinafter, medical practitioners shall
supplement the summary after the patient's visit. If significant
information regarding the patient is also located in another
medical entry, the summary shall contain an indication where the
relevant information is located. Diagnosis or assessment of the
condition must not be indicated repeatedly during one and the
same medical treatment.
19. A patient can become familiar with information, which is
included in the medical entries regarding him or her and stored
in a medical treatment institution, by visiting the doctor
providing medical treatment in a medical treatment institution.
The duty of the doctor providing medical treatment is to provide
information regarding the diagnosis of the patient, examination
and treatment plan, regarding other treatment methods and
prognosis of the disease included in the medical entries in an
understandable way and also to explain the meaning of the content
of the entries made in the medical documents.
20. [20 September 2011]
21. If the doctor providing medical treatment or the head of
the medical treatment institution has determined, that a part of
the medical entries contains information which is to be specially
protected, it shall be kept separately on technical information
carriers. In such case the place of location of the relevant part
of information shall be indicated in the medical entry.
22. The head of the medical treatment institution shall ensure
protection of the medical entries and information included
therein against deletion, amending of facts and unauthorised use,
and shall assign a medical practitioner responsible for the
protection of the medical entries and information included
therein (hereinafter - the responsible person).
23. Medical practitioners of the medical treatment institution
involved in the medical treatment process of a patient shall,
during working hours, ensure that persons, which are not involved
in the medical treatment process, cannot access the medical
entries of the patient and information included therein.
24. Out of the working hours of a medical treatment
institution the medical entries of the patient and information
included therein shall be stored in a separately locked room or
locked cabinets, which do not provide access to persons not
involved in treatment process. The keys of the room or cabinets
shall be kept by the responsible person.
IV. Quality of the Medical
Entries
25. The medical entries shall be true, complete, clearly
legible and without corrections.
26. Entries in medical documents may be made only by medical
practitioners. Reports regarding examinations carried out for a
patient, which are drawn up electronically, shall be signed by
the doctor providing medical treatment and they shall be appended
to the medical entries. If a medical document is drawn up
electronically in conformity with the laws and regulations
regarding drawing up electronic documents, the document details
"signature", "date" and "stamp" shall not be completed. Only
completed sections of the medical documents drawn up
electronically may be printed out on a paper.
[15 April 2008; 25 November
2014]
27. In order to certify performance of instructions by the
doctor providing medical treatment in the health care of a
patient, a medical practitioner shall indicate obvious facts in
the medical entries. Entries provided in medical documents by a
medical practitioners other than doctors shall be determined in
the internal rules of procedures of a medical treatment
institution. Symbols and abbreviation may be used only in those
cases which are provided for in the internal rules of procedures
of a medical treatment institution.
28. Pathomorphological reports, and also description of the
operation and epicrisis shall be printed, except for the
epicrisis regarding care at home.
[20 September 2011]
29. A medical entry is regarded to be fully completed, if it
contains all necessary parts laid down in this Regulation,
including epicrisis or final entry, and if all final diagnoses
and complications have been entered.
30. If due to justified reasons corrections are to be made in
the medical entries, retention of initial information included in
the medical entries and adding thereof to the corrections shall
be ensured.
V. Medical and Register Documents
to be Used in Medical Treatment Institutions and Time Periods for
Storage Thereof
[25 November
2014]
31. Inpatient medical treatment institutions shall use the
register documents referred to in Annexes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15, 18, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 26, 28, 29, 30,
32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 83, 85, 89,
90, 91, 94 and 104 to this Regulation.
[16 February 2016]
32. Outpatient medical treatment institutions shall, according
to their profile of activity, use the register documents referred
to in Annexes 12, 15, 18, 19, 20, 22, 23, 24, 26, 30, 32, 39, 40,
41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 49, 51, 53, 57, 58, 60, 61, 84, 85,
89, 90, 91, 92, 94, 95, 96, 99, 100, 101, 102 and 103 to this
Regulation.
[16 February 2016]
32.1 An outpatient medical treatment institutions
may in conformity with their profile of activity use the register
documents referred to in Annex 16 and 93 to this Regulation.
33. Medical treatment institutions other than those referred
to in Paragraphs 31 and 32 of this Regulation shall use the
register documents which are referred to in Annexes 62, 63, 64,
66, 68 and 85 to this Regulation.
34. Medical treatment institutions shall use the standard
medical documents referred to in Annexes 54, 59, 70, 73, 75, 76,
77, 79, 80, 81 and 88 to this Regulation.
34.1 The medical treatment institution of the
National Armed Forces may use the documents referred to in Annex
40 and 100 to this Regulation also outside the territory of
Latvia.
[29 September 2015]
35. The medical entries which are provided:
35.1. in the documents referred to in Annexes 5, 10, 15, 18,
24, 28, 29, 39, 40, 41, 53, 63, 75, 83 and 100 to this Regulation
shall be stored for one year after the last entry;
35.2. in the documents referred to in Annexes 8, 36 and 37 to
this Regulation shall be stored for two years after the last
entry;
35.3. in the documents referred to in Annexes 26, 62 and 85 to
this Regulation shall be stored for three years after the last
entry;
35.4. in the documents referred to in Annexes 4, 7, 9, 11, 23,
32, 38, 42, 45, 46, 51, 58, 60, 66, 68, 79, 80, 81, 82 and 91 to
this Regulation shall be stored for five year after the last
entry;
35.5. in the documents referred to in Annexes 6, 57, 90 and 99
to this Regulation shall be stored for 10 years after the last
entry;
35.6. in the documents referred to in Annexes 1, 13, 19, 20,
22, 43, 44, 59, 76 and 77 to this Regulation shall be stored for
15 years after the last entry;
35.7. in the documents referred to in Annex 61 to this
Regulation shall be stored for 25 years after the last entry;
35.8. in the documents referred to in Annexes 2, 3, 30, 34,
35, 47, 49, 64, 70, 73, 84, 93 and 95 to this Regulation shall be
stored for 75 years after the last entry;
35.9. in the accompanying check of the document referred to in
Annex 64 to this Regulation shall be stored for one year.
[29 September 2015; 16 February
2016]
35.1 Images obtained by radiological manipulations
(in radiodiagnostic films or in electronic form) shall be stored
for 10 years.
VI. Closing Provisions
36. Paragraphs 19, 31, 32, 33 and 34 of this Regulation shall
come into force on 1 July 2006.
37. Paragraphs 20 and 24 of this Regulation shall come into
force on 1 January 2007.
38. The register forms referred to in Annexes 5, 10, 19, 21,
24, 26, 29, 40, 41, 51 and 61 to this Regulation, which have been
acquired before 31 December 2011, may be used no longer than
until 31 December 2012.
[20 September 2011]
39. The register forms referred to in Annexes 12, 45, 46, 63,
76, 77, 83, 90 and 91 to this Regulation, which have been
acquired before 1 January 2014, may be used no longer than until
31 December 2014.
[10 December 2013]
40. The register forms of medical documents referred to in
Annexes 32, 40, 41 and 51 to this Regulation, which have been
acquired before 1 January 2015, may be used no longer than until
30 June 2015.
[25 November 2014]
41. The register form of a medical document referred to in
Annex 40 to this Regulation, which has been received before 1
October 2015, may be used until 1 October 2016.
[29 September 2015]
42. The register forms of medical documents referred to in
Annexes 30, 35, 39, 42, 90 and 99 to this Regulation, which have
been acquired before 1 March 2016, may be used no longer than
until 1 August 2016.
[16 February 2016]
Prime Minister A. Kalvītis
Minister for Health G. Bērziņš
Annex 93
Cabinet
Regulation No. 265
4 April 2006
[20 September
2011]
| Name of the
medical treatment institution |
|
Code
         |
|
I. Physical and
mental development assessment sheet for a child from 1 week to 5
years of age1
| 1. Given name,
surname |
|
|
2. Date of the birth (dd.mm.yyyy) |
  . .   . .     . . |
3. Personal identity number
      - -      |
| 4. Gender
(mark as appropriate) |
1
- male; 2 - female |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Weight at the birth _______ g |
height ________ cm |
head circumference ________ cm |
| Weight at
the discharge ________ g |
| Labour/Apgar
score |
Family
anamnesis |
Risk factors (including
genetic) |
|
| Child's age |
1 week |
3 weeks |
1 month |
| Date of the
visit |
  . .   . .     . .
(dd.mm.yyyy) |
  . .   . .     . .
(dd.mm.yyyy) |
  . .   . .     . .
(dd.mm.yyyy) |
| Physical development (in
addition see physical development curves in Chapter II,
Sub-paragraph 1 or 3, correct, if the child is born before
week 37) |
| Weight (g) |
(if possible) |
(if possible) |
|
| Height (cm) |
|
|
|
| Head circumference (cm) |
|
|
|
| Complaints from the parents |
|
|
|
| Feeding2; 3 |
Breastfeeding (exclusive) 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula
150 ml/kg/d 
Nature of laxation

Passing of urine

|
Breastfeeding (exclusive) 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula 150 ml/kg/d 
Nature of laxation

Passing of urine

|
Breastfeeding (exclusive) 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula 150 ml/kg/d 
Nature of laxation

Passing of urine

|
| Educating and
advice2; 3 |
TRAUMA
PREVENTION |
Safety of the baby's bed 
Sleeping position/bed
sharing/sleeping in the parents' room 
Car seat (infant) 
Emergency telephone numbers

CO/smoke detector

Suffocation/safe toys 
Hot water < 49 °C

Safety of weapons 
|
| |
BEHAVIOUR AND FAMILY
ISSUES |
Sleep/crying 
Assess the necessity to apply
for a home visit by a social care provider 
Eating habits of the mother 
Brothers and sisters 
Consolation/sympathy 
Family conflicts/stress 
Parental responsibility/upbringing 
Parent tiredness/depression 
|
| |
OTHER ISSUES |
Passive smoking 
Do not use medicinal products
against cough/reducing cold symptoms 
Temperature
control/appropriate clothes 
Ask regarding use of
alternative medicine 
Discuss the use of a teat

Sun exposure/sun protection products/insect repellents

Fever control 
|
| Information to
parents3 |
|
|
Immunisation programme 
Use of antipyretics 
|
|
Development2; 3
Absence of any feature determines further assessment of
the development.
Correct, if born before week 37
|
Sucking reflex 
Reflector reaction of leg support/automatic stepping

When lying on the belly, turns the head from the middle
position to the side 
|
Good breast sucking 
Reflector reaction of leg support/automatic stepping

When lying on the belly, turns the head from the middle
position to the side 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
Focuses sight 
Reacts to a loud or sudden
sound 
Good breast sucking (grip and position of the breast)

When lying on the belly, lifts the head 
Calms down at the feeling of
comfort 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
| Clinical examination2;
3 It is recommended to carry out clinical examination
appropriate to the age in each visit |
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Skin (jaundice, dryness)

Fontanelle 
Red reflex examination of eyes
with ophthalmoscope 
Heart/lungs 
Navel/liver 
Femoral pulse 
Hips 
External genitals/
testicles 
Care of foreskin of a boy/urine jet 
Muscular tonus 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Skin (jaundice, dryness)

Fontanelle 
Heart/lungs 
Navel/liver 
Femoral pulse 
Hips 
External genitals/testicles 
Care of foreskin of a boy/urine jet 
Muscular tonus 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Skin (jaundice)

Fontanelle 
Corneal light reflex

Heart 
Hips 
Muscular tonus 
|
| Problems, plans2; 3; 4;
5 |
Screening result of phenylketonuria (PKU) and congenital
hypothyroidism (CHT) 
Hearing examination with otoacoustic emissions method
- testing result 
|
Red reflex examination of eyes with ophthalmoscope, if
it has not been carried out previously 
Hearing examination with otoacoustic emissions
method, if it has not been carried out previously

|
Red reflex examination of eyes with ophthalmoscope, if
it has not been carried out previously 
Hearing examination with otoacoustic emissions
method, if it has not been carried out previously

|
| Health group |
1  2 2  3 3  |
1  2 2 3 3  |
1  2 2  3 3  |
| Immunisation2 |
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
| Doctor's signature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Child's age |
2 months |
3 months |
4 months |
6 months |
| Date of the visit
(dd.mm.yyyy) |
  . .   . .     . . |
  . .   . .     . . |
  . .   . .     . . |
  . .   . .     . . |
| Physical development (in
addition see physical development curves in Chapter II,
Sub-paragraph 1 or 3, correct, if the child is born before
week 37) |
| Weight (g) |
|
|
|
(x 2 birth weight) |
| Height (cm) |
|
|
|
|
| Head circumference
(cm) |
|
|
|
|
| Complaints from the
parents |
|
|
|
|
| Feeding2;
3 |
Breastfeeding (exclusive breastfeeding/mostly
breastfeeding/partly breastfeeding) 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula 
|
Breastfeeding (exclusive breastfeeding/mostly
breastfeeding/partly breastfeeding; discuss causes for
hypogalactia) 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula 
|
Breastfeeding (exclusive breastfeeding/mostly
breastfeeding/partly breastfeeding) 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula 
|
Breastfeeding 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula 
Exclude food allergies 
Fruit/vegetables 
Assess necessity of food containing iron (cereal, meat)

Do not give egg white, nuts, honey 
Do not give sweetened liquids 
Do not give a bottle in the bed 
Safe food (choking prevention) 
|
|
Educating, advice2; 3 |
TRAUMA
PREVENTION |
Car seat (infant) 
Sleeping position/bed
sharing/sleeping in the parents' room/safety of a bed

Poisons/emergency telephone
numbers 
Electrical switches/sockets

CO/smoke detectors

Suffocation/safe toys 
Safety of weapons 
Hot water < 49 °C/bathtub
safety 
Falling (stairs, baby
walkers, baby changing table) 
|
| BEHAVIOUR AND FAMILY
ISSUES |
Sleep/crying/waking up at night 
Parental responsibility/upbringing 
Assess the necessity to apply
for a home visit by a social care provider 
Consolation/sympathy 
Parent tiredness/depression 
Family conflicts/stress 
Brothers and sisters 
Returning at work/necessity of a nanny 
|
| OTHER ISSUES |
Passive smoking 
Teething/teeth care/fluorine 
Fever control 
Temperature
control/appropriate clothes 
Food quality (pesticides) 
Discuss the use of a teat

Sun exposure/sun protection products/insect repellents

Ask regarding use of
alternative medicine 
Do not use medicinal products
against cough/reducing cold symptoms 
Read aloud 
|
| Information to
parents3 |
|
|
Immunisation programme 
Use of antipyretics 
|
|
|
Development2; 3
Absence of any feature determines further assessment of
the development.
Correct, if born before week 37
|
Follows to a movement with eyes 
Makes sounds and crows
("chats" or intonative screaming) 
When applied to a shoulder of
an adult, holds the head 
Likes touches and cuddles

Replies with a smile 
When eating two or several
sucking episodes before swallowing 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
With eyes and turning the head above centre line, follows
to a movement 
"Social smile" 
The first strings of syllables 
Is stable when supporting on forearms 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
Laughs/shrieks in a dialogue with parents 
Answers to people with
excitement 
Holds stable his or her head,
if he or she is supported on a shoulder or put in a seating
position 
Accepts position on the belly 
Makes rhythmic strings of syllables (sounds)

Holds a subject for a short
time period, if it is put in a hand 
Follows moving toy or person
with eyes 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
Turns his or her head to the direction of a sound

Follows a moving object 
Babbling/makes syllables in different sound volume,
tonality 
Shows joy or dislike with his
or her voice 
Replies with a voice when
somebody speaks with him or her 
Support on opened palms in the position on the belly

Rolls from back to belly and
vice versa 
Sits with a support

Reaches/grasps toys

Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
| Clinical
examination2; 3 It is recommended to carry out
clinical examination appropriate to the age in each
visit |
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Fontanelle 
Heart 
Hips 
Muscular tonus 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Fontanelle 
Red reflex examination of
eyes
with ophthalmoscope

Light reflex of cornea 
Ask about hearing

Heart 
Hips 
Muscular tonus 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Fontanelle 
Ask about hearing

Hips 
Muscular tonus 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Fontanelle 
Red reflex examination of eyes
with ophthalmoscope 
Corneal light
reflex/examination of strabismus with cover test

Ask about hearing

Hips 
Muscular tonus 
|
| Problems,
plans2; 3 |
Red reflex examination of eyes with ophthalmoscope,
if it has not been carried out previously 
Corneal light reflex examination, if it has not
been carried out previously 
Hearing examination with otoacoustic emissions
method, if it has not been carried out previously

|
|
Red reflex examination of eyes with ophthalmoscope,
if it has not been carried out at 3 months of age

Corneal light reflex examination, if it has not
been carried out at 3 months of age 
|
|
| Health group |
1  2 2  3 3  |
1  2 2 3 3  |
1  2 2 3 3  |
1  2 2  3 3  |
|
Immunisation3 |
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
| Doctor's
signature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Child's age |
9
months
(additional check-up from 7 to 11
months) |
12 months |
15 months |
| Date of the visit
(dd.mm.yyyy) |
  . .   . .     . .
  . .   . .     . . |
  . .   . .     . . |
  . .   . .     . . |
| Physical development (in
addition see physical development curves in Chapter II,
Sub-paragraph 1 or 3, correct, if the child is born before
week 37) |
| Weight (g) |
|
|
(x 3 birth
weight) |
|
| Height (cm) |
|
|
|
|
| Head circumference (cm) |
|
|
(approximately 47
cm) |
|
| Complaints from the parents |
|
|
|
|
| Feeding2; 3 |
Breastfeeding 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula 
Do not give a bottle in the bed 
Do not give sweetened beverages 
Cereal, fruit, vegetables, meat/alternatives

Getting familiar with cow's milk products 
Do not give egg white, nuts, honey 
Safe food (choking prevention) 
|
Breastfeeding 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula or 2 % cow milk 
Encourage to use a cup instead of a bottle 
Lower appetite 
Safe food (choking prevention) 
|
Breastfeeding 
D vitamin 10 micrograms
(400-900 IU/per day) 
Formula or 2 % cow milk 
Encourage to use a cup instead of a bottle 
Safe food (choking prevention) 
|
| Educating and
advice2; 3 |
TRAUMA
PREVENTION |
Car seat (infant/child) 
Poisons/emergency telephone
number 
Safety of weapons 
CO/smoke detectors

Electrical switches/sockets

Suffocation/safe toys 
Hot water < 49°C/bathtub
safety 
Falling (stairs, baby walkers) 
|
| |
BEHAVIOUR AND
FAMILY ISSUES |
Sleep/crying/waking up at night 
Parental responsibility/upbringing 
Assess the necessity to apply
for a home visit by a social care provider 
Consolation/sympathy 
Parent tiredness/depression 
Family conflicts/stress 
Brothers and sisters 
Necessity of a kindergarten/babysitter 
|
| OTHER ISSUES |
Passive smoking 
Teething/teeth care/fluorine/dentist 
Fever control 
Food quality (pesticides) 
Discuss the use of a teat

Sun exposure/sun protection products/insect repellents

Ask regarding use of
alternative medicine 
Environment (lead)  Footwear Footwear  Active and healthy
lifestyle/environment Active and healthy
lifestyle/environment 
Do not use medicinal products
against cough/reducing cold symptoms 
Read aloud 
|
| Information to parents |
|
|
|
|
Development2; 3
Absence of any feature determines further assessment of
the development.
Correct, if born before week 37
|
Seeks after hidden toys 
Uses clear double-syllables

Reacts differently to
different people 
Uses sounds to pay attention
to himself or herself 
Sits without a support

Stands with holding on to
something 
Plays social games (touches
his or her nose) 
Reaches to be hold up 
Puts thumb and pointing finger together 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
Responds to his or her name 
Understands simple
instructions 
First words or syllables with a meaning 
Tries to pronounce 3 or more
words (may be unclear) 
Crawls or slips 
Stands up/stands freely 
Walks with holding on
something 
Shows emotions according to a situation 
Grasps a tiny object with a thumb and bent pointing
finger 
Reacts painfully to parting
from parents/carer 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
Tries to pronounce 5 or more words (may be unclear)

Tries to obtain something with help of sounds or
gestures 
Grasps and eats with fingers

Crawls some steps up the
stairs 
Shows fear from strange
people/places 
Tries to squat to take a toy from the floor 
Takes off socks, tries to open shoelaces 
Makes a pyramid of two blocks 
Watches the reaction of adults in order to understand
how to react (when falling down himself or herself)

Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
| Clinical examination2;
3 It is recommended to carry out clinical examination
appropriate to the age in each visit |
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Fontanelle 
Ask about hearing

Hips 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Fontanelle 
Ask about hearing

Size of tonsils/teeth 
Hips 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Fontanelle 
Ask about hearing

Size of tonsils/teeth 
Hips 
|
| Problems, plans2;
3 |
Red reflex examination of eyes with ophthalmoscope,
if it has not been carried out at 6 months of age

Corneal light reflex/
examination of strabismus with cover test, if it
has not been carried out at 6 months of age 
|
Haemoglobin
concentration in blood  |
Examination by an oculist (once in 13-24 months of
age) 
Red reflex examination of eyes with
ophthalmoscope, if examination by an oculist has not
been carried out 
Corneal light reflex/examination of strabismus with
cover test, if examination by an oculist has not been
carried out 
|
| Health group |
1  2 2  3 3  |
1  2 2 3 3  |
1  2 2  3 3  |
| Immunisation3 |
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
| Doctor's signature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Educating and advice2; 3 |
TRAUMA
PREVENTION |
Car seat (child) 
Bathtub safety 
Suffocation/safe toys 
|
Car seat (child) 
Protective helmet/protectors

Emergency telephone number

CO/smoke detectors

Safety-matches 
Safety on water 
Safety of weapons 
|
|
|
BEHAVIOUR AND FAMILY
ISSUES |
|
|
Parent/children contact 
Discipline/restrictions 
Parent tiredness/stress/depression 
High social risk child 
|
Parent/children contact 
Discipline/restrictions

Parent tiredness/stress/depression 
High social risk child

Brothers and sisters 
Family conflicts 
|
|
|
OTHER ISSUES |
| |
Socialisation/role games 
Teeth care/dentist

Learning to use a toilet/hygiene 
Break using of a teat

Read aloud 
|
Teeth care/fluorine/dentist 
Ask regarding use of
alternative medicine 
Active and healthy lifestyle/environment 
Passive smoking 
Learning to use a toilet/hygiene 
Assess readiness for
pre-school institution/school 
Socialisation possibilities 
Sun exposure/sun protection products/insect repellents

Food quality (pesticides) 
Environment (lead) 
Do not use teat 
Do not use medicinal products
against cough/reducing cold symptoms 
Read aloud 
|
| Information to parents |
|
|
|
|
Development2; 3
Absence of any feature determines further assessment of
the development.
Correct, if born before week 37
|
Usually the child's behaviour can be controlled easily

He or she has interest about
other children 
Usually he or she can be
calmed down easily 
Seeks for support when in
sorrow 
Indicates to several
different body parts 
Tries to attract attention in
order to show something 
Turns when his or her name is
called 
Indicates to something he or
she wants 
Seeks a toy when he or she is
asked to do it 
Imitates speech sounds
knowingly 
Pronounces 20 or more words
(may be unclear) 
Can say three different consonants 
Walks freely 
Eats with a spoon unaided

Takes off a bonnet/socks
unaided 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of
the child 
|
2 years
At least one new word per week 
Two-word sentences

Understands one or two-stage
instructions (take the small ball and give to mummy)

Makes two steps backwards
without a support 
Tries to run 
Puts an object in a small
container 
Imitates his or her parents
(gives a doll to drink) 
Continues to acquire new skills 
Parents have no concerns
regarding development of the child 
|
4 years
Understands related
directions to three sides 
Asks many questions and
replies (what are you doing?) 
Uses simple compound sentences 
Stands on one leg 1-3 sec. 
Goes up the stairs by
alternating feet 
Draws people with at least three body parts 
Uses the toilet during the day 
Opens buttons and
zip-fastener 
Tries to calm down somebody
who is sad 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
|
3 years
Understands two-stage and
three-stage instructions (take the hat and shoes and put
them in the wardrobe) 
Uses sentences with 5 or more
words 
Goes up the stairs with
adding step, by holding to handrails 
Twists off lids from
dishes/turns switches 
Plays behaviour games with
actions and words (pretends that he or she is cooking,
repairing a car) 
Spends a short period of time together with known people
without parents/carer 
Turns over book pages one by one 
Imitates writing movements 
Draws a circle 
Listens to music or stories for 5-10 min. together with
an adult 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
5 years
Counts aloud or on fingers in
order to answer "how many?" 
Knows basic colours and forms 
Speaks clearly for the most
part of the time 
Uses complex sentences 
Throws and catches a ball

Is engaged with one activity for 20-30 min. alone

Can dress himself or herself
with minimum assistance 
Shares willingly 
Hops on one leg 
Retells episodes of a story

Easily parts from
parents/carer 
Parents have no concerns regarding development of the
child 
|
| Clinical examination2;
3 It is recommended to carry out clinical examination
appropriate to the age in each visit |
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Fontanelles are closed 
Ask about hearing 
Size of tonsils/teeth 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Red reflex examination of eyes
with ophthalmoscope/vision sharpness 
Corneal light
reflex/examination of strabismus with cover test

Ask about hearing 
Size of tonsils/teeth 
Blood pressure 
|
Physical examination of all organ systems 
Special attention:
Ask about hearing 
Size of tonsils/teeth 
Blood pressure 
|
| Problems, plans2;
3 |
Examination by an oculist, if it has not been
carried out previously 
Red reflex examination of eyes with
ophthalmoscope, if examination by an oculist has not
been carried out 
Corneal light reflex/examination of strabismus with
cover test, if examination by an oculist has not been
carried out 
|
Examination by an oculist at 3 years of age 
Dental hygienist at 2 years of
age 
Dental hygienist at 3 years of
age 
Consultation of a speech therapist/audio speech
therapist, where necessary 
|
Dental hygienist at 4 years of age 
Dental hygienist at 5 years of
age 
Red reflex examination of eyes with
ophthalmoscope/vision sharpness, if examination by an
oculist has not been carried out at 3 years of age

Corneal light reflex/examination of strabismus with
cover test, if examination by an oculist has not been
carried out at 3 years of age 
Consultation of a speech therapist/audio speech
therapist, where necessary 
|
| Health group |
1  2 2  3 3  |
1  2 2  3 3  |
1  2 2  3 3  |
| Immunisation3 |
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
According to vaccination calendar 
Additional vaccination 
|
| Doctor's signature |
|
|
|
Notes.
1 Adapted, by using Leslie Rourke, Denis
Leduc and James Rourke "Rourke Baby Record" of May,
2006, and August, 2009.
2 Degree of evidence: in bold - proved good; italic
- proved on average; standard - without evidence, but there is a
consensus (agreement) by specialists.
3 Designations when completing a card: √ -
no problem, X - a problem.
4 Screening of phenylketonuria (PKU) and congenital
hypothyroidism (CHT) shall be carried out on 4th-5th day of
life.
5 Hearing examination with otoacoustic emissions
method shall be carried out on 3rd-4th day of life. Pay attention
to children who are born in planned out-of-hospital labour,
because examination of children born in a hospital is carried out
in a labour ward.
II. Norms of
physical development of children
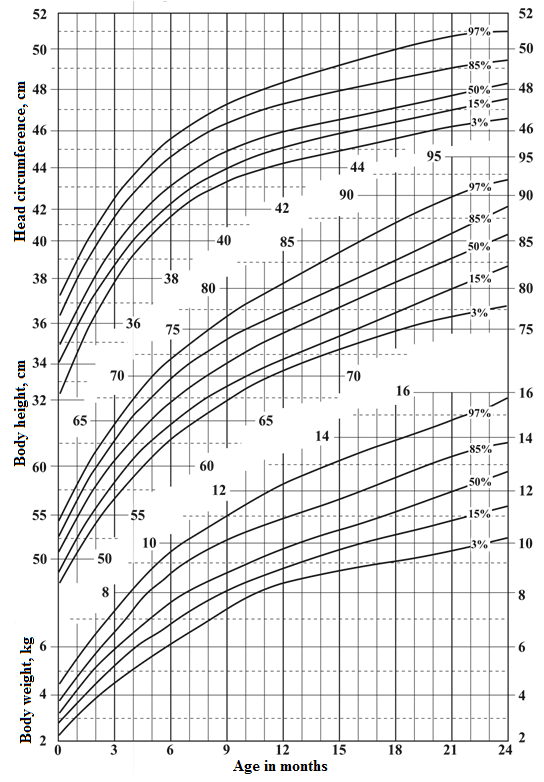
1. Percentile card of girls' head circumference, body height
and body weight from the birth until 24 months of age
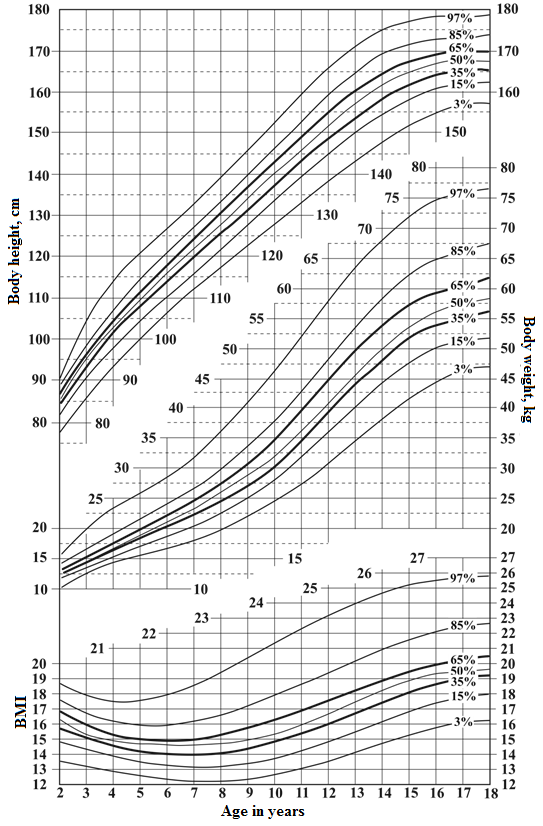
2. Percentile card of girls' body height, body weight and BMI
from 2 until 18 years of age
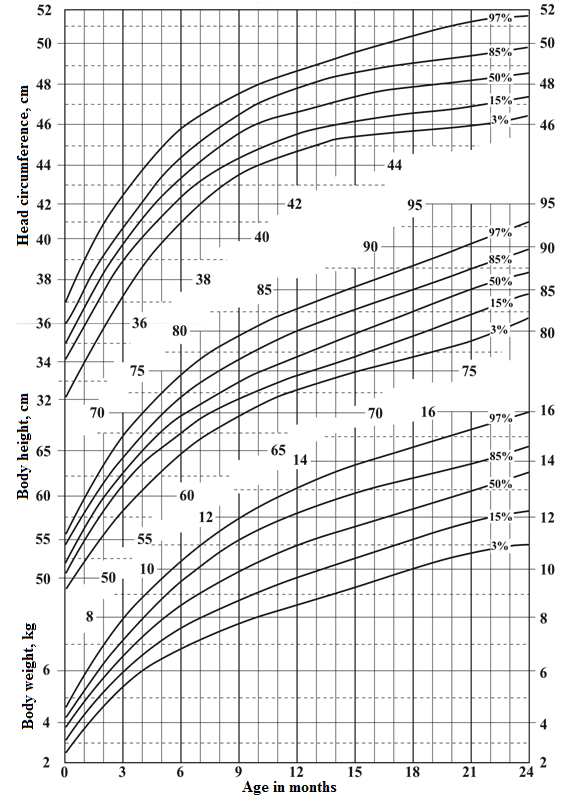
3. Percentile card of boys' head circumference, body height
and body weight from the birth until 24 months of age
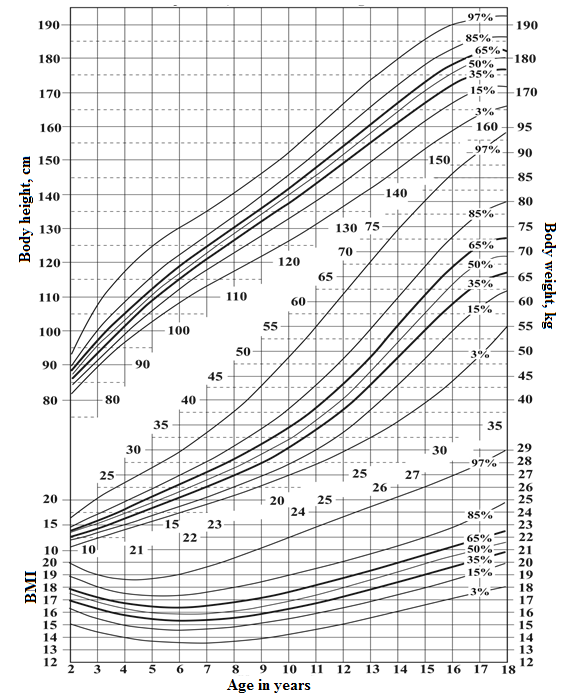
4. Percentile card of boys' body height, body weight and BMI
from 2 to 18 years of age
Translation © 2017 Valsts valodas centrs (State
Language Centre)




